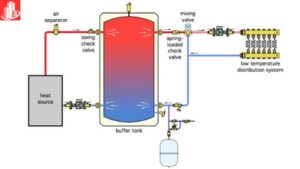
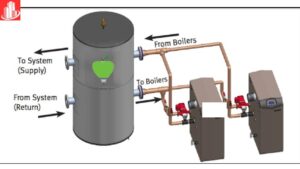
A buffer tank works by storing extra water to keep heating or cooling systems stable. It absorbs sudden changes in water temperature, helping to balance flow and prevent strain on the system, making everything work smoothly and efficiently.
Imagine a system that keeps your heating or cooling steady, even when demand changes quickly. That’s what a buffer tank does! By holding extra water, it balances temperature and flow, helping your system run smoothly and efficiently.
Stay with us to learn how buffer tanks keep your heating or cooling system steady. We’ll explain how these tanks balance water flow and temperature, making sure everything works smoothly so you stay comfortable without any hassle.
Purpose of a Buffer Tank
Buffer vessels are a vital part in control of fluctuation in the temperatures used in heating and cooling. This kind of system tends to cycle with regard to the energy demands.Without a buffer tank, such variations lead to inefficiencies and uneven temperature control. The tank acts as a reservoir that stores or releases heat when needed, ensuring consistent performance.
Thereby virtually eliminating the workload, pressure and stress on equipment in the process, buffer tanks stabilize the system. This minimizes cycling of boilers, heat pumps or chillers since independent cycling prolongs their life span. Further, the constant flow of hot or cold water is energy saving and appropriate for users as it enhances the quality of water supplied.
Components of a Buffer Tank
Buffer tanks are simple in design. Key components include:
- Tank Shell: Typically made of steel, designed to handle pressure.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: Let water enter the body and let it out also.
- Insulation Layer: It minimizes heat transfer to surrounding environment.
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor water temperature inside the tank.
Some tanks also include a stratification plate. It helps maintain layers of hot and cold water. This improves thermal efficiency.
Working Principle
The buffer tank balances energy supply and demand. When the system generates more energy than needed, the tank stores it. When demand exceeds supply, the stored energy is released.
For instance:
- A heat pump might generate heat intermittently. The buffer tank stores this heat. It then supplies it steadily to the system.
- In cooling systems, the process works in reverse.
The temperature inside the tank is monitored using sensors. When the water cools or heats beyond a set point, the system activates. This ensures stability.
Applications of Buffer Tanks
Buffer tanks are widely used in hydronic heating systems. It is important for you to know that these systems depend on the tanks to raise efficiency of boilers besides providing steady heat. It is the most important component of solar heating systems, the use of which allows to have in stock the accumulated solar heat during the day at night or in inclement weather.
In chilled water systems, buffer tanks ensure consistent cooling. They absorb excess chilled water during low demand and release it when the cooling requirement increases. These applications highlight the versatility of buffer tanks in various energy systems.
Advantages of Using Buffer Tanks
Using buffer tanks brings multiple benefits to energy systems. One significant advantage is improved efficiency. The tank eliminates the frequent cycling of various system components hence reducing both energy usage and costs. It also prolongs the operational life expectancy of equipment by reducing mechanical stress coupled with frequent on off cycles.
Another benefit is maintaining a consistent temperature. The variation in heating and cooling is regulated by the tank since it stores the energy surplus and then let it out when required. This affords the user maximum comfort and at the same time improves on the reliability of the system.
Sizing a Buffer Tank
The size of the buffer tank depends on the system requirements. We can c calculate it by using the following formula :
V=Q⋅Δt ÷ ρ⋅cp
Where:
- V = Volume of the tank (m³)
- Q = Heat load (kW)
- Δt = Desired temperature change (°C)
- ρ = Water density (1000 kg/m³)
- cp = Specific heat capacity of water (4.18 kJ/kg°C)
Types of Buffer Tanks
Buffer tanks come in different types to suit various applications. Single-circuit tanks are ideal for systems with one energy source. Dual-circuit tanks can handle two energy sources simultaneously, offering greater flexibility in mixed-energy setups.
The kind that allows different zones for both hot and cold water for better results is known as the stratified tanks. High pressure uses pressurized tanks to provide for the pressure without compromising on safety or the life of the system. The decision on the type of tank that needs to be used in a particular energy system has to be made according to the nature of that particular system.
Key Features of Modern Buffer Tanks
Modern buffer tanks are equipped with advanced features. These improve performance and usability.
- Digital Temperature Controls: It provides precise monitoring and adjustments.
- Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Enhance durability.
- Modular Designs: Allow for easy installation and expansion.
Some models also integrate smart controls. These communicate with the main system for optimal efficiency.
Advantages of Proper Placement
Depending upon the position that one affixes to the generator, determines the performance of the buffer tank. Ideally, which means that, the tank should be placed in an area with high temperatures to reduce heat loss. Proper insulation around the tank further reduces energy wastage.
Easy access for maintenance is another important consideration. Location of the tank makes it easy to clean, inspect, or attend to any mechanical issues which may arise. If placed in the right manner then the users will be confident that the tank will perform in the right manner and even have a longer lifespan.
Common Problems and Solutions
Buffer tanks, while reliable, can encounter some issues. Sediment buildup inside the tank is a common problem. This can reduce the tank’s efficiency over time. Daily cleaning is necessary to avoid forming deposits on different sections of the flexor.
Another problem is corrosion, and this is common in tanks, which have the wrong floor coating. Using anti-corrosion treatments or materials can resolve this. Discrepancy in temperatures may result from low-quality sensors, and this can be corrected by adjusting or replacing the sensors in question.
Integration with Other Systems
Buffer tanks are designed to integrate seamlessly with other energy components. In solar heating systems, they store surplus energy generated during peak sunlight hours. This stored energy is then available during periods of low sunlight.
In HVAC arrangements, buffer tanks are in conjunction with chillers and boilers in that they ensure steady heating or cooling. Integration at the proper time improves system performance, their power consumption, and reliability when introduced in different weather conditions.
Conclusion
It helps to know how buffer tanks capture this fact which can make a large impact in keeping a steady heating or cooling system. These tanks also assist in fluctuating temperature changes and balancing water flow while they use more space to store extra water. This eliminates undue pressures on the system, cutting on the usage and breakdown frequencies hence enhancing durability.
Once you understand the functioning of the buffer tanks, you realize that they serve a purpose of making the indoor environment to be friendly to occupy or spend time in and also make systems to operate as expected. Good buffer tanks are an effective solution in hydronic and HVAC systems where changeability is not a desirable characteristic. Whether it’s for a home or commercial setting, these tanks provide stability and efficiency, saving energy and ensuring reliable operation. A buffer tank might just be the component that helps your system perform at its best for years to come.
FAQs
What is the principle of a buffer tank?
A buffer tank operates by storing extra water to absorb sudden changes in temperature. This helps keep heating and cooling systems stable and efficient.
What is the difference between a storage tank and a buffer tank?
While a storage tank holds water solely for future use, a buffer tank temporarily stores water to balance temperature and flow, making heating and cooling smoother.
What is the difference between a buffer tank and a thermal store?
A buffer tank stabilizes temperatures by absorbing fluctuations, whereas a thermal store supplies hot water by storing energy from multiple sources, like solar or biomass.
How is a buffer tank more effective than a hot water tank?
Unlike a hot water tank, a buffer tank reduces system strain by balancing temperature changes, which improves efficiency and lowers wear over time.
How do buffer tanks work?
Buffer tanks hold extra water to absorb temperature shifts, ensuring steady flow. This helps maintain efficient heating and cooling, even with fluctuating demand.
Click On This Link : Understanding Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)