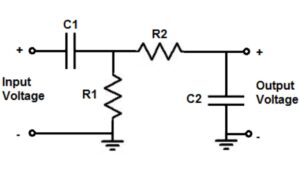
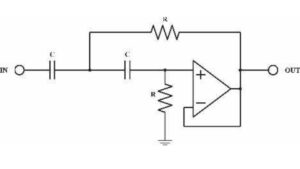
A high pass filter allows high-frequency signals to pass through while blocking lower frequencies. It is widely used in audio processing, electronics, to reach the cleanness of sound, eradicate noise and to accent particular details, making it critical to obtain clean sound.
Have you ever been writing a transcript for a particular podcast and thought, how do I make my audio better? A high pass filter might be the simple solution. It helps you focus on the important sounds by blocking out low-frequency distractions, improving overall clarity.
Please standby while we discuss high pass filters. In this article, we’ll explain how they operate, why they are beneficial, and how you can benefit from getting better sound and signal processing, which will clear up the raw audio into more precise and focused sounds.
What is a High Pass Filter?
A high pass filter is an electrical device utilized in filtering circuits to permit frequencies beyond a certain value to pass on while preventing lower frequencies from passing through. It works by setting a specific cutoff frequency. Frequencies above this point are allowed, while lower ones are reduced. This makes high pass filters essential for refining sound or signals in many industries.
They are common in audio processing, electronics, and communications. For example, in audio systems, they remove unwanted background noise like hums or rumbles. In electronics, they help clean up signals to make data clearer.
How Does a High Pass Filter Work?
High pass filters work by separating frequencies based on a threshold. This threshold is called the cutoff frequency. Signals below this frequency are suppressed, while higher signals are allowed to pass.
The filter’s design determines how sharply it separates frequencies. A steep filter sharply blocks low frequencies, while a gentle filter reduces them gradually. This characteristic depends on the filter’s “order,” which controls the slope of the cutoff.
Types of High Pass Filters
There are following two main types of high pass filters: passive and active.
-
Passive High Pass Filters
These use basic components like resistors, capacitors, or inductors. They don’t need external power and are simple to design. However, they cannot amplify the signal and might reduce its strength.
-
Active High Pass Filters
These include an operational amplifier (op-amp) in the circuit. In Active filters it can amplify signals and provide good performance. They are widely used in modern electronics for high-quality results.
Key Features of a High Pass Filter
High pass filters have several important features:
- Cutoff Frequency: Determines which signals are filtered out.
- Order of the Filter: Defines the slope or sharpness of the cutoff.
- Gain: Indicates how much the signal is amplified or reduced.
- Impedance: Reflects the resistance of the filter to signals.
These features help in designing a filter tailored to specific needs. For instance, a steeper filter may be used in critical applications like medical devices.
Designing a High Pass Filter
Designing a high pass filter starts with identifying the desired cutoff frequency. This depends on the application. For instance in the audio processing, suppose you reserved the cutoff at 80 Hz which will filter a low frequency noise.
Next, decide the filter type. Passive filters are simple and cost-effective. Active filters, however, are better for applications requiring signal amplification. Finally, choose the components. Capacitors, resistors, and op-amps should be selected based on the frequency range.
Applications of High Pass Filters
High pass filters are used in a variety of industries. Their ability to clean up signals and focus on useful data makes them invaluable.
- Audio Processing: Removing low-frequency noise, like rumble, to improve sound clarity.
- Telecommunications: Filtering out interference in signal transmission.
- Medical Devices: Enhancing ECG and EEG signals by removing noise.
- Image Processing: Improving details by sharpening high-frequency edges.
These applications show how high pass filters make systems more efficient and effective.
High Pass Filters in Audio Processing
Audio engineers rely heavily on high pass filters. These filters remove unwanted low-frequency sounds, such as wind noise or hums from recordings. It improves the clarity and makes the audio more professional and better for the listeners.
In live sound systems, high pass filters help manage bass frequencies that can overpower other sounds. They are also used in microphones to capture clean, high-quality audio by blocking out unnecessary low-frequency noise.
Importance of High Pass Filters in Communications
In telecommunications, high pass filters ensure signal clarity. They eliminate low-frequency interference that can disrupt data transmission. For instance, telephone systems use these filters to focus on human speech frequencies.
They are also crucial in radio systems. High pass filters block unwanted noise, allowing clearer signals to reach the receiver. This ensures better communication quality in various fields, including aviation and military.
High Pass Filters and Medical Technology
High pass filters are vital in medical devices. In ECG machines, they remove low-frequency noise caused by patient movement or electrical interference. This ensures the heart’s signal is clear and accurate.
Similarly, EEG devices use high pass filters to refine brain wave signals. By blocking unwanted frequencies, they help doctors make precise diagnoses. These filters are crucial for high-quality medical care.
High Pass Filters in Image Processing
High pass filters aren’t limited to audio and signals; they also enhance images. In image processing, they focus on high-frequency details like edges and textures. This makes images sharper and more detailed.
For example, photographers use high pass filters in editing software to sharpen photos. By emphasizing fine details, these filters improve visual quality and make images more appealing.
Choosing the Right High Pass Filter
The choice of a high pass filter depends on your application. First, consider the cutoff frequency. For audio, a lower cutoff may be sufficient. For medical or communication purposes, a higher cutoff might be necessary.
Next, decide on the type of filter. Passive filters work well for basic needs. Active filters are better for more demanding applications. Always consider the balance between cost, complexity, and performance when selecting a filter.
The Future of High Pass Filters
High pass filters are evolving with technology. Modern filters are becoming more precise and efficient. Digital high pass filters are now common, offering greater flexibility and customization.
As industries demand better performance, high pass filters will continue to improve. Their applications in audio, communications, and medical technology will expand, making them even more essential in the future.
Conclusion
High Pass Filters are among the most important filters when it comes to filtering of audio signals and signals in general. Thus by merely passing frequencies higher only they filter out noise with frequencies lower than the desirable ones thereby improving the sound quality. If you are involved in audio restoration, whether it is music, voice recordings, electronic signals etc. it will help to know how High Pass Filters can be employed.
Finally, High Pass Filters are used by almost all industries including sound and video production, telecommunications and many more. Their ability to refine sound and eliminate interference makes them indispensable. With a clear understanding of how they function, you can confidently apply High Pass Filters to your projects, ensuring a cleaner, more focused output every time.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a high-pass filter?
High-pass filters are mainly designed to transmit signals with higher frequencies and to reject signals with lower frequencies. This also aids in the reduction of interference such as low frequency noise or hum that may interfere with the operation.It’s widely used in audio and signal processing to improve clarity.
2. What is the rule of a high-pass filter?
This kind of filter is used in a similar method to the following: It passes frequencies above the cutoff frequency. Frequencies below this cutoff are reduced or blocked. The rule is simple: low frequencies get filtered out, and high frequencies stay intact.
3. What are the specifications of a high-pass filter?
The key specifications include:
- Cutoff frequency: The frequency below which signals are blocked.
- Order of the filter: The steepness of the cutoff.
- Impedance: The filter’s resistance to signals at various frequencies. These factors determine the filter’s performance and suitability for different applications.
4. What should my high-pass filter be?
Your high-pass filter should be designed to suit your needs. Consider the cutoff frequency that blocks unwanted noise but lets through necessary high frequencies. Also, choose the filter order for how sharp the cutoff should be. It should match the application.
5. What are the real-life applications of high-pass filters?
High-pass filters are used in various real-life applications, such as:
- Audio: Removing low-frequency noise like hum in recordings.
- Telecommunications: Eliminating interference in signals.
- Medical: Enhancing ECG signals by blocking noise.
- Image processing: Sharpening images by removing low-frequency blur. They improve signal quality in many fields.
Also Click On It : Nyquist Plot: What Is It? Stability Criteria and Key Terminologies