Capillary tube refrigeration is a system where a small narrow tube controls flow of the refrigerant in cooling systems. When the refrigerant moves through the chamber it cools as it expands and thus helps cool fridges and A/C cars.
follow this link to learn how your refrigerator can stay cool without complex machine mechanisms. The secret lies in very small things like the capillary tube. This is no more than a really thin pipe, but it works a lot to help your food stay cold and fresh!
Please follow us as we take you through a detailed insight and an analysis of capillary tube refrigeration. This fundamental but essential part is a mainstay of many coolants, allowing your machines to work effectively, preserving your meals and beverages.
What is Capillary Tube Refrigeration?
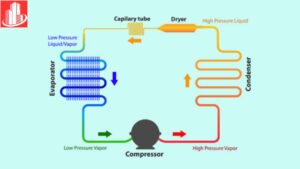
Capillary tube refrigeration can be described as where a small diameter tube is used to control the flow of the refrigerant in the refrigeration system. In most homes, it’s used in refrigerators, air conditioners, and any other appliance that has a cooling action. It is therefore part of a large system which controls the pressures of the refrigerant hence cooling the air or preserving the food. It simply consists of a space that decreases the pressure of the refrigerant flowing through it whereby that refrigerant evaporates and in the process captures heat. In so doing, the refrigerant records a lower temperature to cool the space or the appliance within which it is located.
The workings of this capillary tube are relatively easy and it is a truly designed tube. A very small internal bore diameter from 0.5mm to 2mm ensures that it is suitable for applications in small refrigeration systems. Due to pressure drop, the narrowness of the tube produced a resistance that was not healthy for the gasses. It is the decrease in pressure allowing the refrigerants to vaporize and to do so it is important for it to pull heat from the surroundings. However, unlike thermostatic or electronic expansion valves, the capillary tube does not require input of any other kind of power or instructions to operate. This makes it a durable and an energy preserving mode of transport.
How Does the Capillary Tube Work?
The refrigerant in high pressure liquid form enters the capillary tube from the condenser section of the circuit. Considering the fact that the tube is rather very thin in diameter, it is well understood that it narrows down leading to sudden pressure drop as the refrigerant is passed through the tube. This pressure drop is critical in the achievement of the refrigerant phase change process. When the pressure drops then the liquid refrigerant begins to transform into cold gas and starts expanding. This cold gas is able to take heat from the environment or the inside of the area or space of the appliance.
The most important function of the capillary tube is to control the flow of the refrigerant from high-pressure side to the low pressure side. And this is important to make sure that the refrigerant has evaporated completely before it’s exposed to the evaporator coil again.After it has passed through this capillary tube, the refrigerant is in the low pressure, cold gaseous state to be able to absorb heat as it circulates in the evaporator.to a sudden drop in pressure as the refrigerant moves through it. This pressure drop is essential for the refrigerant to begin its phase change process. As the pressure decreases, the refrigerant starts to evaporate, turning into a cold gas. This cold gas absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, cooling the area or space inside the appliance.
The capillary tube’s primary job is to regulate the flow of refrigerant from the high-pressure side of the system to the low-pressure side. This ensures that the refrigerant can evaporate fully before entering the evaporator coil. Once the refrigerant has passed through the capillary tube, it is in a low-pressure, cold gaseous state, ready to absorb heat as it circulates through the evaporator.
Benefits of Using Capillary Tube Refrigeration
The major advantage of using a capillary tube in a refrigeration system is that it is so simple in its operation. Unlike other devices that must contain fermions in order to utilize magnetic traps, this does not need other elaborate control mechanisms or power supply; this makes it economically feasible for small and medium power systems. The capillary tube is self-acting and functions depending on pressure differences within the refrigerant. This makes it easy to sustain and difficult to stick as opposed to when using valves that possess extra features that must be adjusted.
The other advantage of capillary tube refrigeration is the low energy use that is required in the entire process. Unlike other systems that rely on external means to control the refrigerant flow, this system consumes minimal power. What makes this an even greener solution is when it comes to appliances that are expected to run indefinitely for instance, refrigerator or air conditioning systems. In addition, the design of the capillary tube is simple and thus has low chances of developing faults, making the system have a longer life span. To homeowners, this simply means cutting down on their maintenance bills besides enjoying long periods without the need to request for repairs.
Applications of Capillary Tube Refrigeration

Capillary tube refrigeration is used in many original refrigeration applications, most commonly in household refrigerators and freezers as well as air conditioners. In such systems, control of the refrigerant flow is made easier and more effective with the aid of the capillary tube. It is most appropriate for small scale systems that do not necessarily require elaborated control and/or other elements. Capillary tube refrigeration finds application in homes and small businesses in the appliances like refrigerators.
Past private and business cooling, slim cylinders are utilized in vehicle cooling and convenient cooling gadgets. These frameworks, known for conservative plans and high cooling limit, depend on fine cylinders. They give a consistent refrigerant inventory while limiting misfortunes.The advantage of this capillary tube refrigeration is its simplicity and that makes it to manufacturers who want to reduce cost in their production.
Capillary Tube vs. Other Refrigeration Expansion Devices
a table comparing the capillary tube with thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs) and electronic expansion valves (EXVs):
| Feature | Capillary Tube | Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) | Electronic Expansion Valve (EXV) |
| Operation | Passive; operates without external energy | Requires sensors and adjusts based on temperature | Requires sensors and controllers; adjusts based on temperature and pressure readings |
| Energy Requirement | None (passive device) | Requires minimal energy for sensor operation | Requires more energy for sensors and electronic controllers |
| Control Precision | Low; fixed flow rate, no adjustments | Medium; adjusts flow rate based on temperature | High; offers precise control based on both temperature and pressure |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High |
| Maintenance | Low; simpler to maintain | Moderate; requires occasional sensor and component checks | High; requires regular maintenance and sensor calibration |
| Best for | Small systems with low capacity and stable cooling needs | Medium to large systems needing moderate control | Large systems or those with fluctuating cooling demands needing precise control |
| Application Complexity | Simple, reliable for basic applications | Moderately complex, suitable for varied load conditions | Complex; ideal for applications with dynamic cooling needs |
| Flexibility and Efficiency | Low flexibility, efficiency limited to basic applications | Moderate flexibility, good efficiency under stable load conditions | High flexibility, highly efficient under variable load conditions |
Limitations of Capillary Tube Refrigeration
While hairlike cylinder refrigeration offers many benefits, its disadvantages ought not be ignored. A key weakness is its impediments in enormous frameworks where exact refrigerant stream control is fundamental. In such frameworks, keeping up with exact and, surprisingly, refrigerant stream — acclimating to changing temperature and strain — is basic. The inactive idea of the narrow cylinder can’t completely fulfill these needs. In this manner, its appropriateness is principally for more modest frameworks as opposed to perplexing, enormous scope applications. This is why enhancing devices like the TXVs or EXVs comes in handy at this stage.
The third limitation is that a small diameter of the capillary tube could undergo blockade and hence restrict the flow of blood. This results in perhaps a restriction on the flow of refrigerant that hampers the refrigeration cycle of the system. As well as, the capillary tube has certain temperature and pressure characteristics; therefore, the system may have stability issues and fluctuation if the equipment is not well maintained. There is a need to check for the capillary tube frequently and to check the amount of refrigerant gas present.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Capillary Tube Systems
Controlling a refrigeration framework with a fine cylinder is less complex than one with development valves. Key upkeep undertakings incorporate checking refrigerant charge and guaranteeing there are no blockages in the cylinder. On the off chance that refrigerant levels are too low, the framework might fail to meet expectations. Then again, overabundance refrigerant can cause overpressure and lower productivity. These fundamental obligations assist with keeping up with ideal framework execution.
In the case of a blockage in the capillary tube, the refrigerant fails to flow fluently; this situation results in low performance or a complete failure of the system. This is usually as a result of intrusions by contaminants or debris or moisture creeping into the system. To rectify this, it is advisable to confirm if there is any obstruction or any defect in the tube. If blockage is discovered then the conduit might require scrubbing or even to be replaced so as to enable the unit’s proper working again. This is true in that normal professional inspections can be able to detect such prospects before they give rise to major effects.
Future of Capillary Tube Refrigeration
In bigger and more complicated frameworks, hairlike cylinders may ultimately be supplanted by further developed extension gadgets. Dynamic frameworks that permit exact administration of refrigerant stream could steadily diminish the utilization of these inactive parts. Regardless of this, slim cylinder refrigeration is probably going to stay a savvy and solid choice for more modest applications. Its effortlessness and effectiveness guarantee it will keep on serving great in smaller frameworks. For the not so distant future, narrow cylinders are supposed to hold their ground as a useful decision in refrigeration innovation.
Future progressions in slender cylinder refrigeration innovation might arise as innovation keeps on advancing. With late advancements in refrigerants, tube materials, and framework plans, the limit of slim cylinders could reach out to bigger and more perplexing frameworks. As the interest for energy-productive and eco-accommodating hardware develops, these advancements could rethink the application scope of narrow cylinders. Furthermore, the crucial plan of the hairlike cylinder stays important for limited scope frameworks, making it versatile to future requirements.
Conclusion
The Capillary Tube Refrigeration remains an ideal choice when it comes to small refrigeration systems since they are cheap, simple and power efficient. That is why it is used in household appliances such as domestic refrigerators and portable coolers without external control and power supply. Though it lacks the precise control found in thermostatic and electronic expansion valves, its durability and low maintenance needs are ideal for steady, low-capacity cooling applications.
Compared to more complex systems, Capillary Tube Refrigeration is an affordable and low-maintenance solution for basic cooling needs. It serves as an efficient option when cooling demands are stable and straightforward, though it may not suit large or highly variable systems. Overall, capillary tubes continue to be widely used in refrigeration systems, balancing simplicity and functionality in an efficient, compact design that remains effective in numerous applications.
FAQs
What is the function of the capillary tube?
The capillary tube controls refrigerant flow in small refrigeration systems. It lowers the refrigerant pressure before it enters the evaporator.
What is the working principle of a capillary tube?
The capillary tube works by creating a pressure drop as refrigerant passes through its narrow tube. This allows it to cool and expand in the evaporator.
What is the difference between a capillary tube and an expansion valve?
A capillary tube is a simple, passive device with a fixed flow rate. An expansion valve adjusts flow based on system conditions, offering better control.
What is the state of refrigerant after a capillary tube?
After the capillary tube, the refrigerant is low-pressure and low-temperature. It’s in a mixed liquid-vapor state, ready for the evaporator.
What is the use of a capillary tube in refrigeration?
The capillary tube is used to maintain pressure drop and control refrigerant flow in small systems. It ensures efficient cooling in compact units like fridges.
Clixck on it : A Guide To The Dual Duct System