Electricity generation is essential for powering homes, industries, and all modern technologies. Different methods are used to produce electricity, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will discuss various types of electric power generation systems, including solar, wind, hydro, coal, and nuclear power. Each of these systems has a unique approach to producing energy, influenced by factors such as location, cost, and environmental impact.
Solar Energy System
Solar energy is one of the most promising alternatives for power generation. It offers a clean, renewable source of energy that harnesses sunlight to produce electricity. There are two main methods of generating electricity from solar energy:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Cells: Photovoltaic cells, typically made from silicon, convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are connected in series or parallel to form a solar panel. When sunlight hits the PV cell, it generates a flow of electrons, producing electricity. PV cells are commonly used in both residential and commercial installations.
- Solar Thermal Energy: Solar thermal systems use mirrors to concentrate sunlight, creating heat. This heat is then used to convert water into steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity. Solar thermal plants are typically larger than PV installations and require ample sunlight to operate efficiently.
Advantages of Solar Energy Systems
- Zero Transmission Cost: For stand-alone solar systems, there is no need for extensive transmission infrastructure, making it ideal for remote areas.
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy does not produce greenhouse gases, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Solar systems require minimal upkeep once installed, reducing ongoing expenses.
- Ideal for Remote Areas: Solar systems can provide electricity in places that are off-grid, improving access to power in rural regions.
Disadvantages of Solar Energy Systems
- High Initial Costs: The setup and installation of solar systems can be expensive.
- Requires Large Space for Bulk Production: Large solar farms need extensive land to capture enough sunlight.
- Weather-Dependent: Solar systems are less effective on cloudy or rainy days.
- Costly Storage Solutions: Solar batteries for energy storage can be expensive, making it difficult to store excess energy for use during non-sunny periods.
Wind Energy System
It is another popular renewable energy source. Wind turbines capture the energy from moving air and convert it into electrical energy. Wind forms when temperature changes in the atmosphere create airflow, and turbines convert this wind into kinetic energy. The turbine’s rotation drives an induction generator, which transforms kinetic energy into electrical power.
Advantages of Wind Energy Systems
- Unlimited and Clean: Wind is a renewable and clean source of energy, available in most areas.
- Low Operating Costs: Wind turbines have nearly zero operating costs once installed.
- Remote Power Generation: Wind turbines can generate electricity in remote areas, making them suitable for off-grid locations.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy Systems
- Inconsistent Power Output: Wind speed varies, making power generation unpredictable.
- Requires Large, Open Spaces: Turbines need ample land to operate without obstructions.
- Noise Pollution: Wind turbines produce noise, which can be a disturbance.
- High Initial Construction Cost: Building wind farms and installing turbines is costly.
- Threats to Wildlife: Turbines pose a risk to birds and other flying animals.
Hydro Energy System
Hydropower is generated by harnessing the energy from flowing water, typically from rivers or oceans. Dams or reservoirs store water, which, when released, flows through turbines, converting kinetic energy into electricity. This method uses gravity to drive water through the system, making it highly efficient and reliable.
Advantages of Hydro Energy Systems
- Instant Availability: Hydropower can be quickly activated to meet demand.
- Multi-Purpose Water Use: After generating power, water can be used for irrigation and other purposes.
- Long-Lasting Infrastructure: Dams have long lifespans, providing power for many years.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Hydropower systems require minimal maintenance after construction.
- No Fuel Transport Needed: Water is readily available, so there’s no need for fuel transportation.
Disadvantages of Hydro Energy Systems
- High Initial Costs: Building dams and reservoirs is expensive.
- Distant Locations: Dams are usually located far from cities, requiring long transmission lines.
- Potential for Flooding: Dam construction can flood nearby towns or habitats.
- Weather-Dependent: Hydropower relies on sufficient rainfall and river flow.
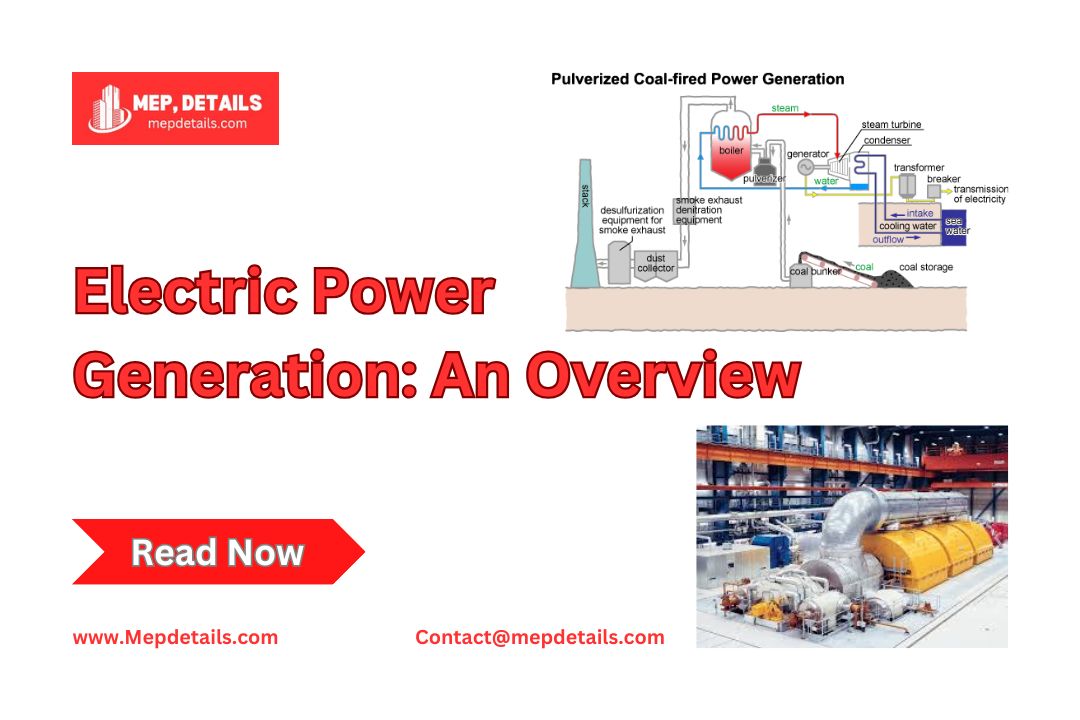
Coal Energy System
Thermal power plants use coal to produce electricity. In a thermal plant, coal is burned in a boiler, generating heat to convert water into steam. This steam, at high pressure and temperature, spins a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. Once the steam has passed through the turbine, it is cooled in a condenser and reused in the boiler.
Advantages of Coal Energy Systems
- Cost-Effective Fuel: Coal is relatively cheap compared to some other fuel sources.
- Lower Initial Costs: Thermal plants generally cost less to build than renewable energy plants.
- Flexible Location: Coal can be transported, allowing thermal plants to be built close to the areas needing electricity.
- Faster Construction: Building a coal plant takes less time than constructing a dam or other major infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Coal Energy Systems
- Non-Renewable: Coal is a finite resource that will eventually be depleted.
- High Operating Costs: Costs fluctuate based on fuel prices.
- Environmental Pollution: Burning coal releases harmful gases and particulates into the atmosphere.
- High Water Demand: Cooling and steam generation require large amounts of water.
Nuclear Energy System
Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear reactions. Instead of coal, nuclear plants use uranium in reactors to produce heat. The heat then converts water into steam, which drives turbines, creating electricity. Nuclear energy is incredibly efficient; just 1 kilogram of uranium can produce as much energy as burning 4,500 tonnes of coal or 2,000 tonnes of oil.
Advantages of Nuclear Energy Systems
- Space Efficiency: Nuclear plants need less land compared to thermal or hydropower plants.
- High Power Output: A single nuclear plant can generate vast amounts of energy.
- Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power does not produce carbon dioxide.
- Small Fuel Requirements: Nuclear plants use minimal amounts of uranium, reducing the need for large fuel supplies.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy Systems
- High Initial Costs: Building a nuclear plant requires a significant investment.
- Expensive to Operate: Maintenance and safety protocols increase operational costs.
- Radioactive Waste: Nuclear plants produce radioactive waste that must be carefully stored.
- High Risk: Nuclear power plants have a risk of accidents and radiation leaks.
Conclusion
Electric power generation has unique applications and characteristics.. Solar and wind energy are clean and renewable but need large spaces and rely on the weather. Hydropower is efficient and lasts long, though it affects local ecosystems. Coal is cheap and easy to use but harms the environment. Nuclear energy is highly efficient but brings safety risks and waste challenges. With technology advancing, renewables like solar, wind, and hydro are becoming better options, and a balanced energy mix can help meet global needs sustainably.
FAQs
What are the concepts of electrical power generation?
Electric power generation uses fuel sources like fossil fuels, nuclear, and renewable energy (solar, wind, hydro) to create energy.
How do you explain the generation of electricity?
Electricity generation uses sources like fossil fuels, nuclear, hydro, geothermal, solar, biofuels, and wind in power plants.
What is power generation in short notes?
Power generation means producing electricity using various technologies, from steam boilers to modern wind turbines.
What is the process of electricity generation?
In a turbine generator, moving fluids push blades to spin a rotor, which converts this motion into electrical energy.
Read More – Nuclear Power Station: A Comprehensive Overview