The Static Kramer Drive controls the speed of an induction motor by injecting opposite-phase voltage into the rotor circuit. This injected voltage increases the rotor’s resistance, which in turn controls the motor’s speed. By adjusting the voltage, both the resistance and speed are regulated. The static Kramer Drive converts the slip power, which is the unused energy between the stator and rotor, into AC power and returns it to the main supply. This method only works when the motor’s speed is lower than the synchronous speed. In this article, we’ll explore the working, construction, and torque-speed characteristics of the static Kramer Drive.
Working of Static Kramer Drive
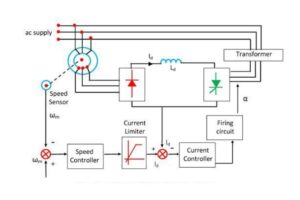
The rotor slip power gets converted into DC by a diode bridge. This DC power then goes into a DC motor, which is mechanically connected to an induction motor. The total torque supplied to the load comes from the combined torque produced by both the induction motor and the DC motor.
The graph below shows how Vd1 and Vd2 change with the speed for two different values of the DC motor field current. When Vd1 equals Vd2, steady-state operation of the drive occurs, at points A and B for field currents If1 and If2.
Speed control is possible only when the speed is less than or half of the synchronous speed. For a wider speed range, the diode bridge is replaced with a thyristor bridge. By adjusting the firing angle of the thyristor amplifier, the relationship between Vd1 and speed can change. This allows for speed control all the way down to standstill.
Construction of Static Kramer Drive
The Static Kramer drive system includes a variable-speed drive system, which uses both a slip ring induction motor and a rectifier-fed direct current (DC) motor.
- Slip Ring: The system recovers slip power through the rectifier and the auxiliary DC motor. The torque applied to the load is the total torque produced by both the induction and DC motors. To regulate high speeds, the system stabilizes the field current of the DC motor.
- Diode: If a wider speed range is needed, the diode bridge can be replaced with a thyristor bridge. This change improves speed control, including the ability to stop the system if necessary.
The Static Kramer drive system, without a line-commutated inverter, produces less reactive power and lower harmonic current components compared to the Static Scherbius system. However, it has a large moment of inertia due to the brushes and commutator of the auxiliary
DC motor, which is a disadvantage. It also has maintenance challenges that make it difficult to manage efficiently.
To control the speed of the induction motor, we must analyze how the inverter operates, converting DC power into variable frequency AC power. Before that, we will first discuss the phase-control scheme used to manage the stator voltage.
Torque-Speed Characteristics of Static Kramer Drive
The torque-speed curve for a motor powered by a static Kramer drive does not produce negative torque once the speed reaches the no-load speed. This happens because the diode bridge creates slip ring voltage.
If the slip exceeds a certain limit for a given injected voltage, the voltage in the rotor circuit, created by the stator, becomes lower than the DC link voltage. As a result, no current flows through the rotor, and no torque is produced.
Conclusion
The Static Kramer Drive offers an efficient method to control the speed of an induction motor by converting slip power into usable energy. Its construction combines a slip ring induction motor with a DC motor, allowing for precise speed control. While the system is advantageous in terms of power recovery and speed regulation, it faces challenges such as maintenance difficulties and a large moment of inertia. By using a thyristor bridge for wider speed ranges, the Static Kramer Drive can offer more flexibility, making it a viable option in various industrial applications.
FAQs
What is a static Kramer Drive?
The static Kramer drive controls the speed of an induction motor by injecting an opposite-phase voltage into the rotor circuit. This injected voltage increases the rotor’s resistance and controls the motor’s speed.
What is a static Scherbius Drive?
The static Scherbius Drive controls the speed of a wound rotor motor below synchronous speed. A diode bridge converts part of the rotor’s AC power into DC. This drive can send power in both positive and negative directions of the injected voltage.
What is a static drive?
A static drive uses a “point-to-point” control system that connects the output pin of the drive IC to the pixel. In contrast, a scan drive uses a “point-to-line” control system.
How does the Kramer system work?
In the Kramer system, slip power is converted into DC power. In the Kramer cascade, this DC power supplies the armature of a separately excited DC motor. The DC motor’s shaft connects to the main shaft through a gear. The DC motor’s back EMF opposes the rotor’s induced voltage in the slip ring induction motor, causing the speed to drop.
Read More – Power Plant: Types, and Their Role in Modern Energy Production