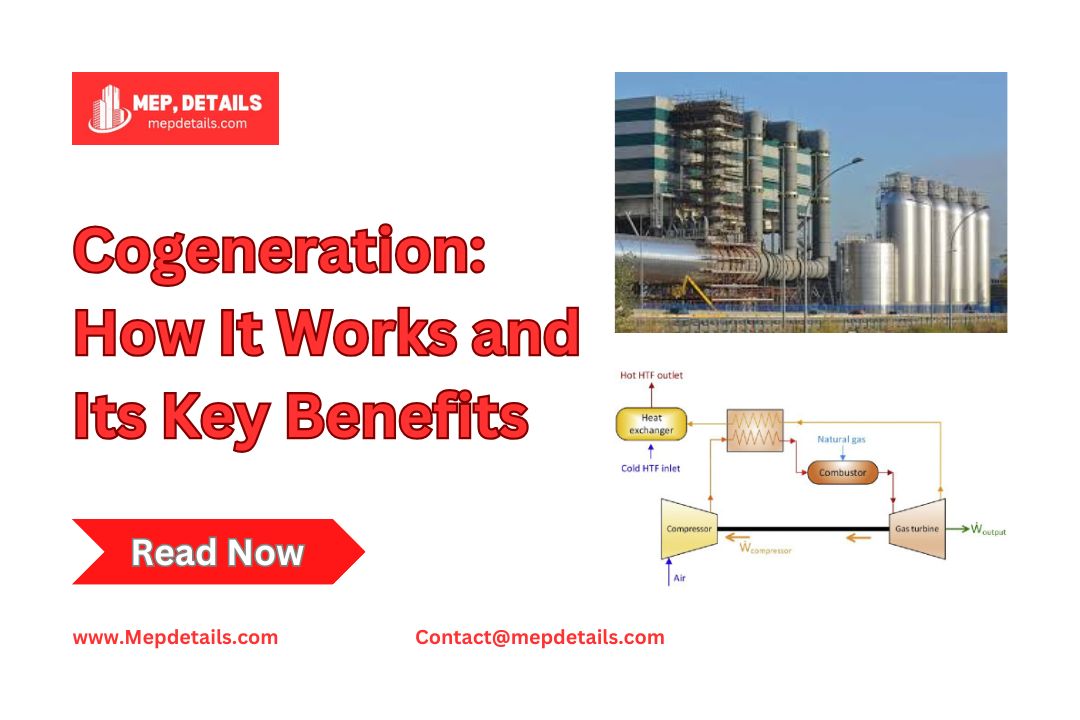
Cogeneration is an energy system that combines heat and power generation to improve efficiency. It captures waste heat from electricity production and uses it for heating or other processes. This method saves energy, reduces costs, and lowers environmental impact. Industries and commercial buildings use cogeneration to maximize energy use and enhance sustainability. In September 2020, the European Commission proposed raising the target for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 from 40% to 55%, with energy efficiency measures like cogeneration playing a key role in meeting these goals. This article will explore how cogeneration works and its benefits.
What is Cogeneration?
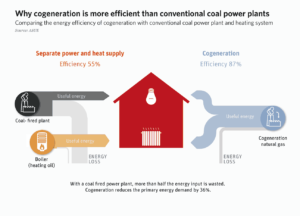
Cogeneration is an efficient technology that generates both electricity and heat at the same time. It is also known as Combined Heat and Power (CHP). Cogeneration currently provides 11% of electricity and 15% of heat in Europe. By using one unit to produce both heat and electricity together, it is more efficient and cost-effective than producing them separately with two different units.
How Does Cogeneration Work?
Cogeneration systems use a main engine, turbine, or fuel cells as the prime mover. This prime mover works with an alternator, when needed, to change the chemical energy in the fuel into electrical energy. Natural gas is the most common fuel, but diesel and hydrogen can also be used.
While producing electricity, the system also generates heat. Instead of letting this heat escape into the air, it is captured and used for useful purposes like heating, cooling, hot water, and industrial processes.
Benefits of Cogeneration
Cogeneration provides several benefits for users and society:
- Increased energy efficiency: Cogeneration is up to 40% more efficient than generating heat and power separately.
- Lower emissions: Cogeneration reduces CO2 emissions by 200 million tonnes each year in Europe. This is the same as the emissions from 42.5 million cars or 2.6 million trucks.
- Reduced energy costs: Cogeneration users enjoy higher efficiency and need less fuel to meet heating and electricity needs.
- Supports renewable energy: Cogeneration can run on renewable fuels, making it the most cost-effective way to use them. Currently, 27% of the fuel used in cogeneration in Europe is renewable, mainly biomass and biogas.
- Empowers businesses and citizens: Cogeneration comes in different sizes, from 1kW to nearly 1GW, making it suitable for all users, from single households to large industrial sites or entire towns.
- Boosts energy system resilience: Cogeneration can provide the exact amount of electricity and heat needed at any given time, adding flexibility and resilience to energy systems. This is especially important as more intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind power are used.
- Cuts transmission and distribution costs: Cogeneration generates heat and electricity at the location, reducing reliance on the grid and avoiding associated grid costs.
- Reduces import dependency: The high efficiency of cogeneration lowers fuel demand in Europe.
- Creates more jobs: The cogeneration sector currently employs 100,000 people in Europe, with job growth expected as the EU invests in energy efficiency and renewables to reduce emissions.
Cogeneration Systems
There are different types of cogeneration systems, depending on the technology used:
- Gas turbine cogeneration: In this system, natural gas is typically used as fuel. The gases produced from burning the fuel are directed into a turbine, which converts mechanical energy into electricity. The leftover energy, in the form of hot gases, can be reused in the industrial process or for other purposes.
- Steam turbine cogeneration: A steam turbine is a machine that converts the energy from steam into mechanical energy. The main benefit of steam turbines is that they can use various fuels, including biomass, coal, natural gas, or municipal solid waste.
- Cogeneration with an internal combustion engine: Internal combustion engines convert chemical energy from fuel into electrical and thermal energy. These engines work by turning a shaft using the back-and-forth movement of pistons. The engine’s shaft is connected to an alternator, which generates electricity. The thermal energy is released as exhaust gases and hot water from the cooling system.
Conclusion
Cogeneration provides a highly efficient solution for generating both electricity and heat simultaneously. It reduces energy costs, lowers emissions, and enhances system resilience. By utilizing waste heat, it increases energy efficiency and supports renewable fuels. It empowers businesses and individuals with scalable systems, from small homes to large industries. As the demand for energy efficiency and sustainability grows, it will play a key role in Europe’s transition to a greener future. Its widespread adoption promises significant environmental and economic benefits for society.
FAQs
What is cogeneration?
Cogeneration means producing both heat and electricity in one system using a single energy source. This process often uses less energy than generating them separately.
Where can you find cogeneration systems?
You’ll often find cogeneration systems in district heating for cities, central heating in large buildings like hospitals, hotels, and prisons, and in industries for heating, cooling, steam production, or CO₂ fertilization.
How does cogeneration work?
Cogeneration creates electricity and heat (like steam) at the same time. Many process plants and small communities use it because it often provides a better return on investment (ROI) than buying energy from a utility.
What are the benefits of cogeneration?
Cogeneration is clean and cost-effective. It uses fuel more efficiently, reducing waste. This process can lower carbon emissions and cut energy costs significantly.
Read More – Electric Power Generation: An Overview