Introduction
Anyone entering signal processing must first master basic signal operations as their initial step. Signal processing operations enable modifications, examination, and enhancement of signals to advance communication efficiency and data processing performance. Toxic relations begin with signal adjustment operations, which engineers as well as electronics specialists use commonly for signal strength modifications and timing and structural modifications. Simple explanations will help us understand each operation in detail.
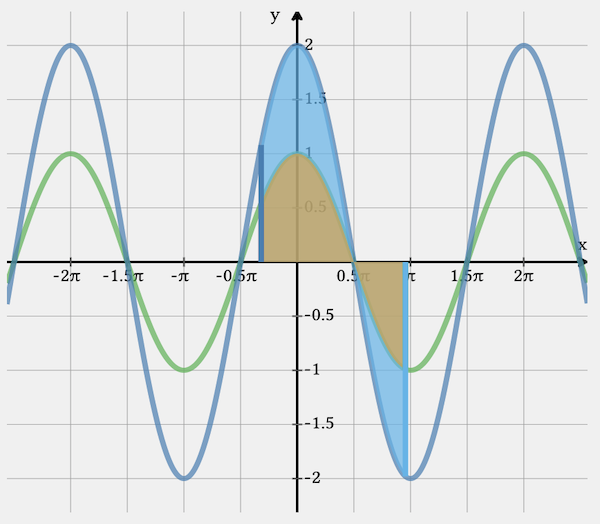
Amplitude Scaling
Amplitude scaling means increasing or decreasing the height (strength) of a signal. To do this, we multiply the signal by a constant value. If this value is greater than 1, the signal is amplified. If it is less than 1, the signal is weakened. This operation is often used to adjust the signal level at the input or output of a system.
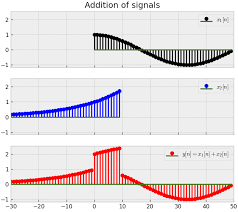
Signal Addition
Signal addition combines two or more signals into one. This is done by adding the signal values at each point in time. This is useful when we want to mix two signals – for example, when adding speech to background music in audio production or combining sensor signals in electronic devices.
Signal Multiplication
Signal multiplication is the point-by-point multiplication of two signals. This is useful in many communication systems. For example, a message signal is often multiplied by a carrier signal to transmit data. This facilitates modulation techniques such as AM (amplitude modulation), where the strength of the carrier signal is varied depending on the message.
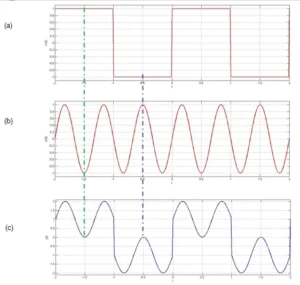
Time Shifting
Time shifting moves a signal forward or backward in time. If a signal is delayed, we shift it to the right. If we want it to appear earlier, we shift it to the left. This is used to synchronize signals or manage delays in a system. It helps to properly align multiple signals during analysis.
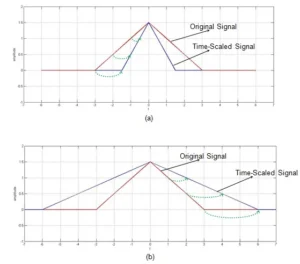
Signal Reflection (Time Reversal)
Reflecting or time-reversing a signal means rotating the signal around a vertical axis. Imagine holding a mirror up to a timeline – the signal will now play backwards. This operation is particularly useful in processes such as convolution, where signals are compared by overlapping.
Conclusion
Basic signal operations such as amplitude scaling, addition, multiplication, time shifting, and reflection are essential for processing signals. These simple yet powerful tools help modify and analyze signals for a variety of real-world applications, such as audio processing, communication systems, and data analysis. By mastering these operations, you can better understand and use complex systems in the digital world.
FAQs
Q1: What are basic signal operations?
A: Amplitude scaling, addition, multiplication, time shifting, and signal reflection are all fundamental signal operations.
Q2: Why is amplitude scaling used?
A: It is used to increase or decrease signal strength for better compatibility with other systems.
Q3: What is time shifting in signals?
A: Time shifting refers to advancing or delaying a signal by moving it forward or backward along the time axis.
Q4: How does signal addition work?
A: Signal addition combines two signals by adding their values at each time point to form a new signal. By adding the values of two signals at each time point, signal addition creates a new signal.
Q5: What is the use of signal reflection?
A: Signal reflection, which is used in analytical techniques like convolution, reverses a signal in time.
Expand your knowledge today! Read our next blog post here!