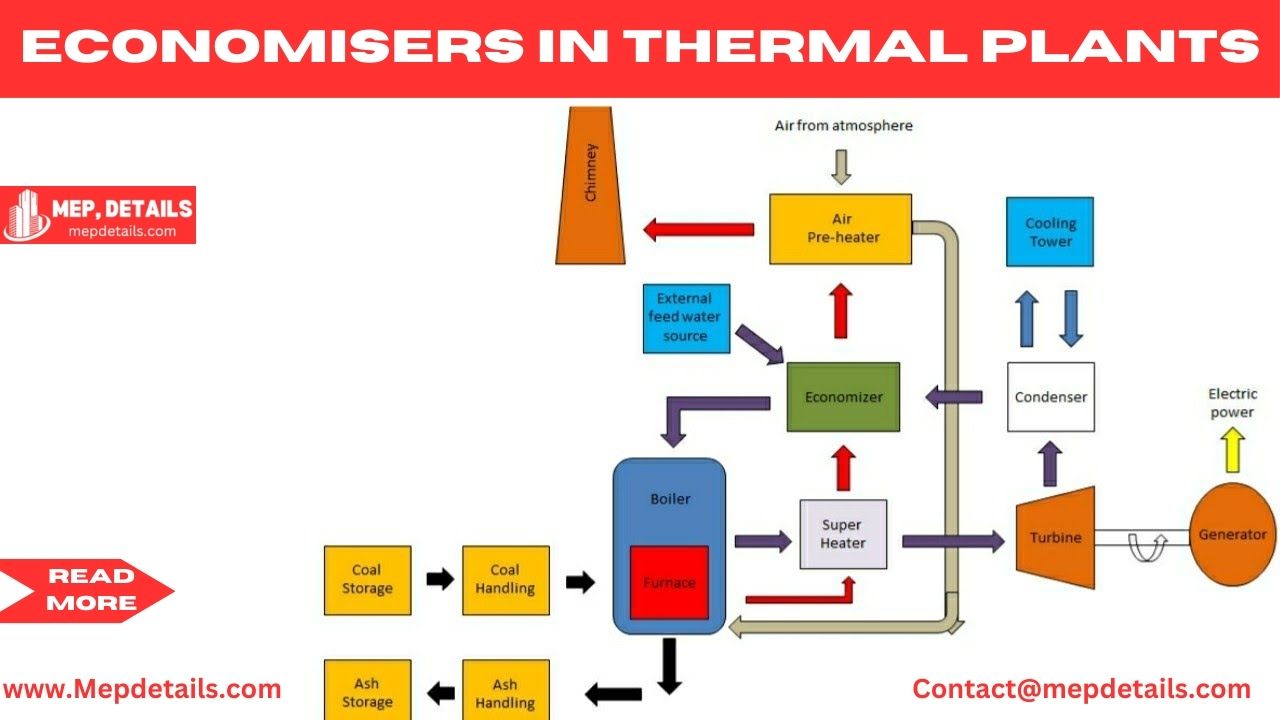
Economisers in thermal plants prevent wastage of energy where exhaust gasses are used to heat feed water before it is taken to the evaporator. This cuts fuel usage, decreases cost, and lowers emissions. It is truly an effective way of improving the process of generation and consumption of power the world over to make it achievable.
Try to picture your company saving fuel and therefore cutting costs and at the same time protecting planet earth.This is made possible by economisers in thermal plants that use waste heat to preheat water. That’s something simple and effective which increases the effectiveness of energy production and therefore makes it more sustainable.
Please read along with us as we describe how economisers can change energy consumption in thermal plants. Discover about this intelligent engineering product how it reduces fuel consumption, cuts expenses, and even increases productivity to where power generation is not only efficient but friendly to mother nature.
The Role of Economisers in Thermal Plants
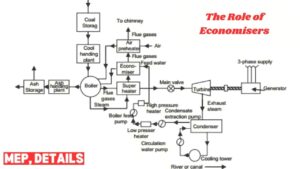
Economisers play an important role to optimize the heat rate of the power plants. Located between the evaporator and the vent gas outlet, these intensity exchangers recover any remaining intensity from fumes and pass them to the feedwater channel before it gets to the heater drum. This intensity recuperation reduces how much fuel necessary to keep steam age; thus, enhancing the plant efficiency. Since economisers reduce the enthalpy expected for steam age, the interaction makes the feedwater preheating more energy-effective.
A very important advantage of economisers is using a lower, more ambiguous amount of fuel, or the SFCSFCSFC, which saves thousands of expense bucks. Furthermore, economisers reduce secondary thermal stresses at the boiler due to the reduction of temperature difference between feed water and the boiler tube. Such reductions in stress will mean that overeem is decreased consequently minimizing material fatigue and thus increasing the life cycle of the more useful components such as the boilers.
That is how Economisers contribute to the optimisation of plant efficiency
The integration of economisers in a nuclear energy station’s Rankine cycle increases by and large heat output. By recuperating heat energy that would somehow or another be squandered, economisers can bring down fuel utilization by up to 15%. This decrease straightforwardly influences working expenses and brings down the ecological impression of the plant by lessening fossil fuel byproducts.
Economisers regularly utilize high warm conductivity materials, for example, carbon steel or cast iron, which work with powerful intensity. A few high level plans integrate finned tubes that grow the intensity move region and work on the proficiency of intensity trade. Preheating feedwater to a higher starting temperature lessens the energy expected in the kettle, further developing the plant’s energy usage rate.
Design and Construction Features of Economisers
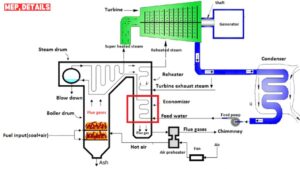
The design of economisers is crucial for their performance and durability. Typically, economisers are constructed using banks of finned or plain tubes that can withstand high operational temperatures and pressure fluctuations. Materials such as low-alloy or stainless steel are often used due to their high resistance to oxidation and thermal fatigue.
To optimize heat transfer, some economisers are equipped with gas flow baffles. These baffles guide the exhaust gasses along specific paths, increasing the contact time between the gases and the heat exchanger tubes. This feature enhances the convective heat transfer coefficient and boosts the overall efficiency of the economiser. For better results, manufacturers often design economisers with extended surfaces and specialized coatings that resist fouling and corrosion.
Key Benefits of Economisers
Executing economisers in warm plants accompanies a scope of advantages:
- Fuel Reserve funds: Decrease in unambiguous fuel utilization (SFCSFCSFC) due to preheated feedwater.
- Functional Expense Decrease: Lower fuel prerequisites lead to huge expense investment funds.
- Discharge Control: Diminished fuel utilization implies less outflows of carbon dioxide and different poisons, supporting consistency with ecological guidelines.
The energy investment funds accomplished by utilizing economisers additionally add to decreasing feedwater treatment costs. Preheated feedwater decreases the risk of thermal shock to the boiler, optimizing chemical reactions and enhancing water quality.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Economisers are susceptible to changes which in turn affect their performance, for instance, fouling from ash and debris stores. Fouling provides warm obstruction thus reducing the intensity transmission rate. Some types of fouling can be prevented through normal support and the utilization of ash blowers and/or sonic cleaning devices.
Another test is erosion particularly when acidic condensate structures due to the cooling of pipe gasses. This issue may be addressed by using consumption safe materials and employing coatings. Furthermore, careful regulation of water science may prevent the formation of new acids, preventing the economiser’s internal surfaces from being damaged and increasing its service life.
Types of Economisers
Economisers are comprehensively characterized into two kinds: non-endlessly gathering. Non-gathering economisers recover moderate intensity from exhaust gases, and these are well suited for applications with slightly high exhaust temperature.Condensing economisers recover both sensible and latent heat and are higher in energy recovery. This type is especially useful where the exhaust gas temperature is comparatively low and the plant can justify the cost of the more costly materials required due to the corrosiveness of condensed flue gasses.
The non-condensing economisers are less complex and cheaper but have a lower effectiveness in comparison with the use of condensing economisers. The use of these types depends on the fuel to be burned, the amount of temperature required in the exhaust, and energy recovery at the plant location.
Maintenance Best Practices
Essential maintenance is required for economisers to function in the most efficient way possible. Such investigations should be aimed at looking for problems such as cylinder leakages, obstruction and concentration. Water washing and mechanical brushing procedures prevent fouling, thus maintaining the intensity to move surfaces clean.
The knowledge of the delta and outlet temperatures and the strain drops may provide indications into the performance of the economiser. Supposing that gross divergences from assumed values are identified it could reveal fractional blockages or scurf which requires attention. Proactive support guarantees that economisers work proficiently, diminishing the probability of unforeseen personal times and costly fixes.
Energy Savings and Mathematical Impact
The energy savings from economisers can be quantified using basic thermodynamic calculations. For instance, if the temperature of the feedwater entering the economiser is TinT_{in}Tin and it exits at ToutT_{out}Tout, the amount of heat recovered can be expressed as:
Qrecovered=m⋅Cp⋅(Tout−Tin)
where:
- mmm = mass flow rate of the feedwater,
- CpC_pCp = specific heat capacity of the feedwater,
- ToutT_{out}Tout and TinT_{in}Tin = outlet and inlet temperatures, respectively.
This recovered energy reduces the heat duty required by the boiler, lowering fuel consumption and enhancing overall plant efficiency.
Future Trends in Economiser Technology
Innovative headways are driving the advancement of additional productive and strong economisers. The incorporation of IoT-based sensors empowers ongoing checking of key boundaries like temperature, tension, and intensity move rates. This information can be dissected for prescient support, limiting impromptu personal times and broadening the economiser’s functional life.
Half breed economisers, which join different intensity recuperation components, are arising as an answer for boost energy usage. These frameworks consolidate numerous intensity trade cycles to recover however much energy as could be expected from the vent gases. The outcome is a higher generally speaking warm effectiveness, supporting the objective of more feasible and harmless ecosystem power age.
The Role of Economisers in Sustainability
Economisers assume a fundamental part in the shift toward more supportable energy creation. By working on the warm productivity of force plants, they assist with lessening the dependence on non-renewable energy sources, bringing down ozone depleting substance emanations. As administrative bodies keep on fixing ecological norms, the utilization of economisers will be key in aiding nuclear energy stations to follow these guidelines while keeping up with productivity.
All in all, economisers are a viable method for upgrading the energy proficiency of nuclear energy stations. Through cautious plan, customary upkeep, and embracing the most recent innovations, plants can expand the advantages of economisers, accomplishing critical energy reserve funds and supporting a more maintainable future for power age.
Conclusion
Maximizing energy savings with economisers in thermal plants is a crucial step toward efficient and sustainable power generation. By capturing waste heat from exhaust gases and using it to preheat feedwater, economisers help lower fuel consumption, reduce costs, and decrease emissions. This simple yet effective technology enhances the plant’s overall performance and supports the push for cleaner energy practices.
Incorporating regular maintenance and adopting advanced materials ensures that economisers work at peak efficiency and last longer. As plants continue to prioritize energy efficiency, economisers play an essential role in balancing operational demands and environmental responsibility. By focusing on maximizing energy savings with economisers in thermal plants, power facilities not only improve their bottom line but also contribute positively to environmental sustainability, setting a strong example for responsible energy production.
FAQs
What is the purpose of economisers in thermal power plants?
The purpose of an economiser in thermal power plants is to recover waste heat from exhaust gasses and use it to preheat feedwater, thereby improving thermal efficiency and reducing fuel consumption.
How do you maximize thermal efficiency?
To maximize thermal efficiency, implement heat recovery systems, optimize combustion processes, and enhance insulation. Regularly maintaining equipment helps minimize heat losses and improve overall performance.
How to increase the efficiency of a thermal power plant?
To increase the efficiency of a thermal power plant, upgrading technology and optimizing operational practices are key. Implementing waste heat recovery systems like economisers and conducting regular maintenance ensure all components function effectively.
How does an economiser improve boiler efficiency?
An economiser improves boiler efficiency by preheating the feedwater using residual heat from flue gases. This process reduces the energy needed for steam generation, lowering fuel consumption and boosting overall efficiency.
What is the main purpose of an economizer?
The main purpose of an economizer is to enhance energy efficiency by recovering waste heat from exhaust gases. This process reduces fuel requirements and minimizes emissions in thermal systems.
READ MORE : Sources of Electrical Energy