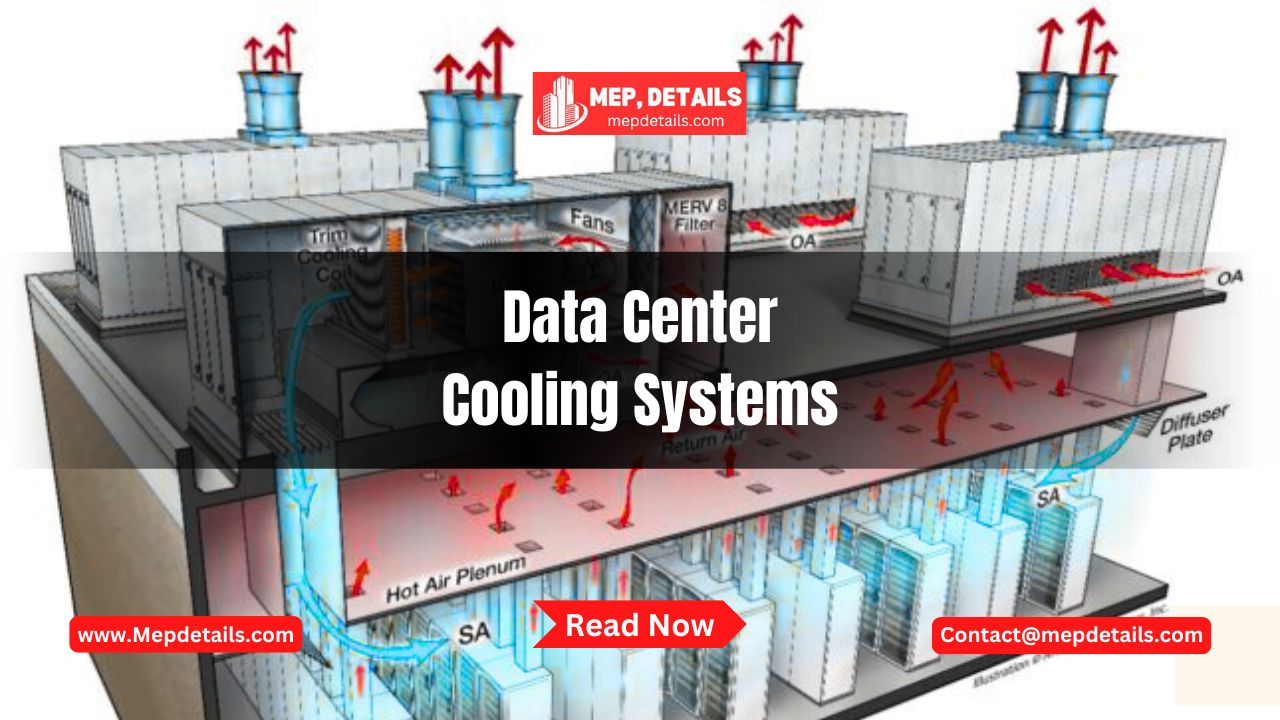
The online world depends on data centers for power. All sorts of online actions such as using apps, websites and paying for items online, are made possible by them. Still, these systems produce a lot of heat and if they do not get enough cooling they may run slower, be damaged or stop functioning. For this reason, data center cooling systems are needed. In this guide, we’ll look at the way these systems function, explain their importance and let you know about today’s cooling technologies.
What Is a Data Center Cooling System?
Keeping the temperature and humidity down to safe limits in a data center is made possible with a data center cooling system. Running computer systems, storage systems and networks at data centers produces a lot of heat. Should the heat not be managed, it could make the equipment very hot and lead it to stop working.
The task of the cooling system is to let hot air out and let in cooler air. They also control airflow so that chilly air goes to the proper equipment and warm air doesn’t blend with it. With this, you can lower the amount of energy used and so, the related expenses.
Why Is Cooling Important in Data Centers?
Protecting the data center’s equipment and ensuring proper protection rely mainly on having efficient cooling. Here’s why cooling matters:
- Protects Equipment: IT equipment may be damaged if it gets very hot and humid.
- Prevents Downtime: Heat-related problems might make servers crash or halt and as a result, important data could be lost.
- Improves Performance: It is easier for machinery to run smoothly for longer when the place is well cooled.
- Saves Money: Fixing or purchasing wasteful systems costs more money to the business.
- Ensures Safety: If the building gets too hot, fire dangers may arise for the people inside.
How Do Data Center Cooling Systems Work?
Heat from the equipment is moved out by the cooling system and cooler air takes its place. There are several ways to do this:
1. Air Cooling
It is usual for both old and smaller data centers to use air cooling. It relies on computer room air conditioners named CRAC or CRAH.
- CRAC: Refrigerants are used in this type of AC to cool the air just like they are in a home unit.
- CRAH: The air conditioner relies on chilled water which results in less energy usage.
In this kind of cooling, chilled air is sent to various spaces through raised floors or open vents. It gets heated by the hot equipment, absorbs that heat and later flows back to the cooling unit for relief.
2. Hot and Cold Aisle Containment
- Cold aisle: This design makes the arrangement of server racks go back and forth in lines.
- Hot aisle: The place where the equipment takes in cool air from outside.
Organizing hot or cold air based on their movements makes the cooling system operate better. Walls or doors help you regulate how air travels in space.
3. Liquid Cooling
Many companies in data center management are turning to liquid cooling because it performs well in high-volume centers. Liquids move heat from a site faster than the same heat moving through an air current.
There are basically two types of control.
- Direct-to-chip cooling: The purpose of tubes is to send liquid to the most heated elements such as CPUs or GPUs and take care of the excess heat.
- Immersion cooling: All servers are put inside a liquid that does not conduct electricity and helps absorb heat.
When you use liquid cooling, you get plenty of power in less space and your equipment takes up less energy.
Popular Cooling Technologies in Use Today
To match their size, location and goals, modern data centers put in place various cooling systems.
1. Free Cooling
The outside air is used in free cooling to cool down the indoor area. It’s more suited to places that are not too warm. The concepts have two types.
- Air-side free cooling: Allows outside fresh air to enter the house.
- Water-side free cooling: Gets assistance from outside cold water for the cooling process.
2. Evaporative Cooling
It is also called swamp cooling, meaning warm air moves through wet pads. When the water evaporates, it lowers the temperature of the room’s air and returns it. There is a better performance when the area is dry and has low humidity.
3. Geothermal Cooling
Basically, geothermal systems rely on the temperature below ground to cool inside the facility. Liquid coolant is put in pipes that are buried underneath the earth. The liquid inside the data center stays at a low temperature because of the ground beneath it and this brings down the air temperature inside.
4. Solar Cooling
Solar energy is able to provide power for thermal-based cooling. This method for heating is eco-friendly and is dependable in places that get a lot of sun.
5. Kyoto Cooling
The system has a rotating thermal wheel that improves the process. Heat is taken out of the data center by cooled air which is pushed back by it. It only takes in a minimal 8% of the energy of standard systems and doesn’t use water.
Smart Cooling Systems and AI
Very often, smart methods are used at modern data centers to keep temperatures low and energy use down.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence monitors the temperature, the level of humidity and the performance of equipment at all times. An air conditioner adapts itself to keep your room cool using less power. A good example of this is Google which cut its data center cooling costs by 40% thanks to AI.
Cooling Robots
There are companies that install sensors inside their server cabinets that can measure internal temperature and send it to the people responsible for facilities. The heat map is made by a method that does not require opening cabinets.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Cooling uses a lot of power—up to 33% of a data center’s energy consumption. In turn, upgrading cooling systems is an effective method to cut expenses and lower carbon emissions.
There are some useful strategies to make work more efficient:
- Make sure to keep HVAC and power systems well maintained on a regular basis.
- Take out inefficient old devices and use newer lights that are energy efficient.
- Use special systems to track the cooling system to quickly discover any weaknesses.
- Take a look at advanced cooling strategies, for example, liquid cooling, geothermal or solar cooling.
Future of Data Center Cooling
When more data centers are built, the cooling for them needs to be more energy efficient and environmentally friendly as well. It is predicted that the cooling market in the U.S. will grow fast during the next few years. Technology will greatly contribute to the increase in green tourism.
In the future, we can expect:
- More companies are using AI in real time for cooling their servers.
- More companies are choosing liquid and immersion cooling.
- Focusing more on the environment by trying natural ways to cool buildings.
- Digital buildings being connected to data centers.
Final Thoughts
Nowadays, data center cooling systems are a necessary element for any facility. They uphold machines, boost their operation, keep costs down and help preserve the environment. Air, liquid and geothermal cooling are only a few of the systems that can be used to suit your specific needs.
Thanks to smart approaches and reliable energy management, data centers can run cool, save money and prepare for upcoming changes. No matter if you are responsible for a big facility or a smaller room, the right cooling solution has a big impact on your long-term plan.
Read More – Water Distribution Systems: Everything You Need to Know