Electricity is a type of energy that comes from other sources like chemical energy, nuclear energy, heat, and solar power found in nature. It happens due to the presence and movement of electric charge in matter. This article will explain the nature of electricity, but first, we will look at what electricity is and how it exists.
Nature of Electricity and Concept of Electricity
Electricity is a common type of energy that we use for many things, like lighting, transportation, cooking, communication, and making products in factories. To understand electricity, we need to learn about the structure of matter. Everything is made of tiny particles called molecules. These molecules are the smallest parts of a substance that still have the substance’s properties. Molecules are made of atoms, which are the smallest parts of an element.
There are two kinds of substances: elements and compounds. Elements have molecules made of the same type of atoms, while compounds have molecules made of different kinds of atoms. To understand electricity, we need to study the atomic structure of these substances.
The Structure of Matter
Electricity plays a key role in modern industrial society, as we use it in many ways, like powering equipment, running motors, providing light, and creating magnetism. To understand electricity, we first need to understand the structure of matter.
In basic physics, we learn that everything in the universe is made of tiny particles called molecules. A molecule holds all the properties of a substance. Each molecule is made up of even smaller particles called atoms. An atom is the simplest form of matter that exists in nature.
Depending on the types of atoms in a molecule, we can classify a substance as either an element or a compound. A substance is an element if its molecule has only one kind of atom, while a compound contains molecules with different types of atoms.
Next, we will explore the structure of an atom and how charged particles like electrons and protons behave to better understand electricity and its nature.
Structure of Atom
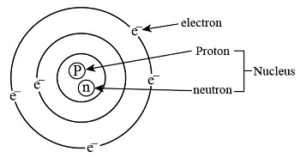
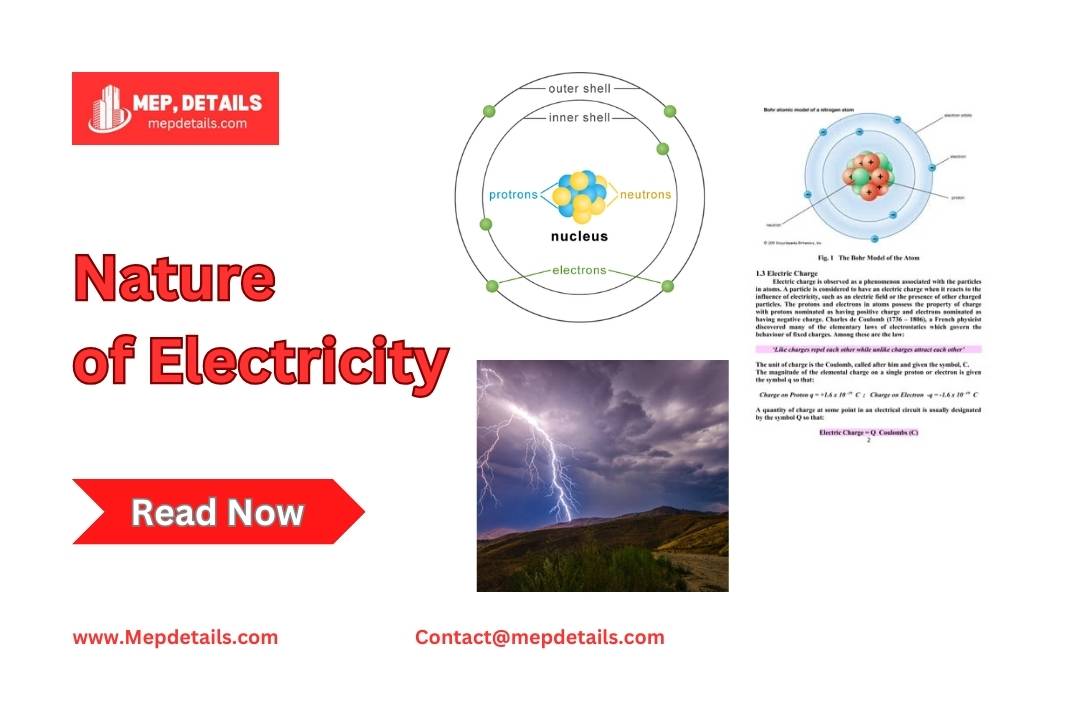
An atom has one central nucleus. The nucleus contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are electrons that have a negative charge. Each electron carries a charge of -1.602 × 10^-19 Coulomb, while each proton has a charge of +1.602 × 10^-19 Coulomb. The positive charge of protons attracts the negatively charged electrons.
Electrons have very little mass compared to the nucleus. Each proton and neutron has a mass about 1840 times that of an electron.
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. If an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion. Conversely, if it gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion. Atoms can also have loosely bound electrons in their outer orbits, known as free electrons. These electrons can detach easily and move around, transferring from one atom to another.
When a substance has more electrons than protons, it becomes negatively charged. When it has more protons, it becomes positively charged. Electricity flows when a negatively charged object connects to a positively charged object through a conductor. The excess electrons move from the negative object to the positive one to balance the charge.
Some materials, like silver, copper, aluminum, and zinc, have many free electrons at room temperature. These materials conduct electricity well because their free electrons can move easily when an electrical potential difference is applied. This movement of electrons in one direction is known as electric current. Generally, we consider current to flow from high potential to low potential, which is opposite to the actual flow of electrons.
Non-metallic materials, like glass and porcelain, have complete outer shells and few free electrons. Therefore, they do not conduct electricity well and are known as insulators.
Conclusion
In this article, we talked about electricity and its nature. Electricity is a common type of energy that comes from electrically charged particles found in all materials. We describe the nature of electricity based on the properties of electric charge. When electricity comes from stationary charges, we call it static electricity. However, when it results from moving charges, we refer to it as current electricity. Additionally, electricity can only flow through conductive materials like silver, copper, and aluminum.
FAQs
What is natural electricity?
Natural electricity exists in different forms in nature. It appears as thunder, lightning, and solar storms on Earth, which help create its magnetic field. Some animals can produce electricity, which they use for protection.
What is the nature of current electricity?
Electric current is the flow of particles that starts when you apply an external voltage to one end of a conductor. This action creates an electric field that pulls negatively charged electrons toward the positive terminal of the voltage source.
What is the fundamental nature of electricity?
Electricity is the flow of electrons through a conductor caused by a difference in electrical potential. Atoms consist of a nucleus with protons and neutrons, and electrons orbit around this nucleus.
What are the characteristics and nature of electricity?
The main characteristics of electricity include voltage, current, resistance, power, and frequency.
Read More – Electric Motor: Types, Benefits, Maintenance