Skip to content
Home » Refrigeration compressor maintenance troubleshooting- Free guide
Maintenance:
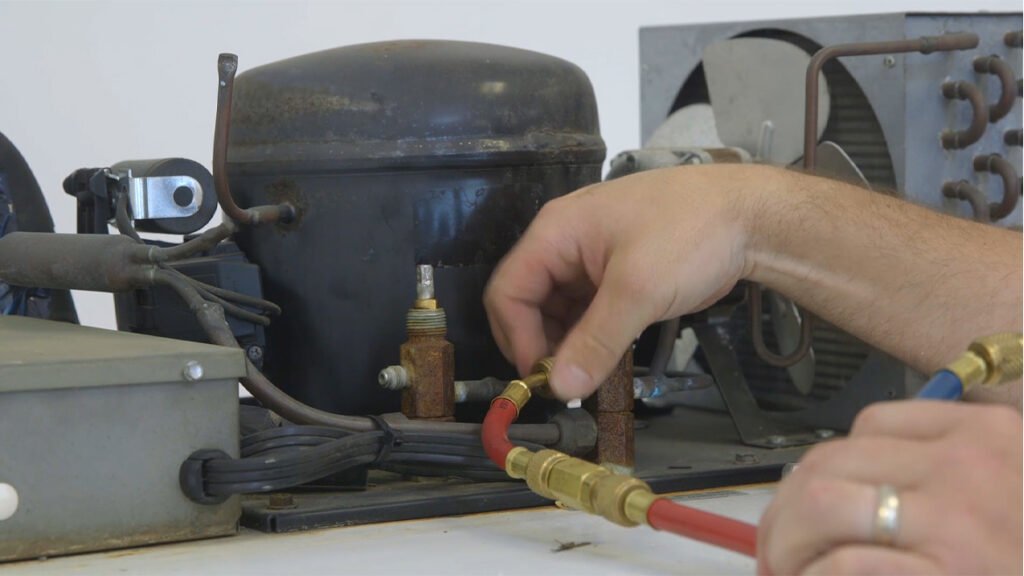
- Regular Inspection: Conduct routine checks on the compressor for any signs of wear, leaks, or unusual noises.
- Cleaning: Keep the compressor and its surroundings clean to prevent dirt or debris from affecting its performance.
- Lubrication: Ensure proper lubrication of moving parts according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Condenser and Evaporator Maintenance: Clean these components regularly to maintain efficient heat transfer.
- Electrical Components: Inspect and tighten electrical connections to prevent loose connections or shorts.
Troubleshooting:
- Poor Cooling: If the system isn’t cooling properly, check for refrigerant leaks, thermostat settings, or issues with the evaporator or condenser.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, knocking, or rattling sounds may indicate mechanical issues or worn-out parts.
- High Energy Consumption: This could result from a variety of issues such as low refrigerant levels, dirty coils, or inefficient compressor operation.
- Compressor Overheating: Check for airflow obstructions, refrigerant issues, or electrical problems that might cause the compressor to overheat.
- Frequent Cycling: Rapid on-off cycling might indicate issues with the thermostat, refrigerant charge, or pressure controls.
error: Content is protected Please fill Free Reach out !!!