Vertical inline pumps are compact, efficient devices used to move liquids in various systems. They save space and energy while ensuring smooth operation. Understanding their design and maintenance helps keep these pumps running well, making our daily lives easier.
Have you ever wondered how water flows smoothly in buildings and factories? Vertical inline pumps are key to this process! These compact machines efficiently move liquids while saving space, making our lives easier and helping industries run smoothly every day.
Stay with us as we explore the fascinating world of vertical inline pumps! We’ll uncover how these efficient machines work, their many uses, and tips for maintenance. Understanding them can help you appreciate the vital role they play in everyday life.
Overview of Vertical Inline Pumps
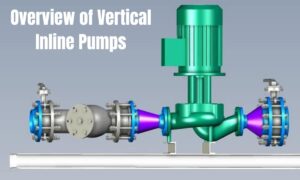
Vertical inline pumps are centrifugal pumps particularly adapted for pumping liquids in a broad range of applications. These pumps are characterized by their vertical orientation, which allows for a compact design that saves space in installation environments. That is because the setup is inline, meaning that the pump is in the pipe, and this reduces installation costs and flow loss.
Vertical inline pumps are usually designed with a motor directly above the pump casing. This design keeps the pump’s shaft vertical, making it possible to mount it directly to the impeller. Thus, vertical inline pumps can run at a high efficiency rate, which is why they are suited for use in HVAC systems, water treatment plants and industrial processes.
Key Components and Design Features
To appreciate the design of the vertical inline pump to the utmost is to know its components. The key parts are the pump body, the impeller, the shaft, the bearings and the motor. The pump case ought not be a pouch where part of the pumped fluid is trapped, but a place where the fluid flows through the pump with little resistance. Because impellers are what drive the pressure needed to pump fluids around, their design can significantly influence the efficiency of the pump.
And, of course, lest the impeller itself be unchallenged in its own uselessness, bearings are to bear on the shaft, to make the engine spin smoothly. The materials from which these components are fashioned are central, since they need to withstand fluctuating pressures and corrosive conditions. Most vertical inline pumps are fitted with wear rings and seals, engineered for long life and low leaks, and capable of operating reliably for years under the toughest conditions.
Applications of Vertical Inline Pumps

Vertical inline pumps are workhorses that dwell in almost every sector. Their principal use today is in HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning) systems, where they pump chilled or heated water through them so people can have comfortable temperatures in their buildings. Their compact design makes them an ideal choice for tight spaces, ensuring efficient heating and cooling without taking up excessive room.
Another common application is in water treatment plants, where pumps help transport and distribute water through the treatment process. Their strength to withstand high flow rates and pressures allows them to be used in municipal and industrial water systems. Another is the use of vertical inline pumps in fire protection systems, which need to provide liquid supply in an emergency.
Benefits of Using Vertical Inline Pumps
Vertical inline pumps have a lot to recommend them, and they can be applied to a wide variety of applications.
- Space-Saving Design: Pumps that are in a vertical line use less space and can be used in places where standard pumps will not fit. This density can also translate to reduced construction expenses and reduced time and effort in installing pipes.
- High Efficiency: Their form minimizes drag by turbulence and pressure, creating the most optimal flow. Even more energy savings are possible with modern pumps that are usually fitted with variable frequency drives (VFDs) that optimise pump speed for demand.
- Reliability: Vertical inline pumps are also very reliable and have a long working life, provided that they are properly maintained.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
There are a few things to keep in mind when specifying upright vertical inline pumps. And it’d better not be bent or the pump won’t work so efficiently. Just a little misalignment can lead to excessive bearing and component wear, prematurely ending the life of the pump. It is also important to factor in the kind of base or mounting platform that is used, because a firm foundation keeps out the kind of vibrations that can compromise performance.
Maintenance is another critical aspect of vertical inline pumps. Periodic checks of components such as seals and bearings must occur to detect wear and possible failures before they become fatal. Perhaps a preventive maintenance program could extend the life of the pump and improve the reliability. Most producers give detailed instructions on how to operate at maximum efficiency if one is to do so.
Challenges in Operation
Vertical inline pumps get the job done, but they aren’t without their own problems. Cavitation, where the pressure inside the pump falls below the fluid’s vapour pressure, is one of the most common. That creates pitting on the impeller and everywhere else, and the pump is ruined. Fittings and installation practices need to be appropriate to prevent cavitation and allow the pump to operate within its intended performance range.
Not to mention being too hot, especially when the pump is on 24 hours a day. Overheating can break seals and bearings, causing early failure. Something should cool it down or something, so that it doesn’t do that, and keep the pump in the temperature range that it can work in.
Comparison with Other Pump Types
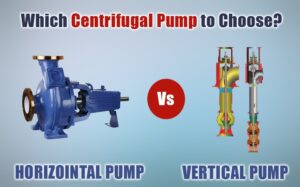
Vertical, inline, line pumps (VILP) are quite different from other pumps, the most familiar, probably, being the horizontal centrifugal pump. Vertical inline pumps offer a more compact design, making them suitable for applications with limited space. They are also more efficient at low flows, which is a plus in many uses.
Alternatively, horizontal pumps might be easier to maintain and replace. They are designed to accommodate more readily available parts, and maintenance operations are far easier. Their disadvantage, though, is that they usually need more complicated piping, and also occupy more space, which is not desirable in tight installations.
Future Trends in Vertical Inline Pump Technology

Technological development and the increasingly desperate search for energy efficiency will characterize the next generation of vertical inline pumps. Equipment manufacturers are developing pumps from more durable materials, and with a better design for low energy consumption. Developments in smart pump technology, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), should also be a significant component.
Smart pumps monitor performance data continuously, and enable predictive maintenance and operation optimisation. With this data-driven approach, it is possible to operate more efficiently, to save on operating expenses, and thus make vertical inline pumps even more attractive for a wide range of applications.
Key Features of Vertical Inline Pumps
| Feature | Description |
| Design | Vertical orientation saves space and improves flow efficiency. |
| Components | Includes casing, impeller, shaft, bearings, and motor. |
| Applications | Used in HVAC, water treatment, and fire protection systems. |
| Benefits | High efficiency, space-saving, and reduced energy consumption. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections and alignment checks are crucial. |
This organized method gives a full picture of vertical inline pumps, their applications and the advantages they offer in various applications.
Conclusion
What you might know about them reveals their vital role in everything from heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) units to industrial applications. They are so compact and so efficient, and they are really needed to save space and power, let alone performance.
It is important to understand what they are made of, and how to maintain them in a working order. Vertical inline pump users can extend the life of their pumps if they have an awareness of issues like cavitation and adhere to good practice. If you want to stay ahead of the curve as technology evolves, you will want to be aware of these pumps if you want to make the right decisions, for your systems and for the planet.
FAQs
How does a vertical inline pump work?
A vertical inline pump works by using a motor to drive an impeller, which creates a pressure difference to move liquid through the pump and into the connected piping system.
What is the principle of vertical pump?
The principle of a vertical pump is based on centrifugal force, where the impeller accelerates the liquid outward, converting rotational energy into kinetic energy to transport the fluid.
What are the disadvantages of vertical pumps?
Disadvantages of vertical pumps include limited flow capacity, susceptibility to cavitation, and potential overheating if not properly maintained or installed.
What are the five points which you will check when a pump is running?
- Check for unusual noises
- Monitor discharge pressure and flow rate
- Inspect for leaks
- Assess motor temperature
- Ensure proper alignment and vibrations.
What is cavitation in vertical pump?
Cavitation in a vertical pump occurs when the pressure in the pump drops below the liquid’s vapor pressure, causing vapor bubbles to form and potentially leading to damage when they collapse.
Click On This: Vertical Inline Pumps: Maximizing Efficiency in Your System