Plumbing has been an important aspect of our modern building, and the cold water system plays an important part within it. This system brings fresh, drinking water to various fixtures of a building. Fresh water was made accessible to residents for drinking, cooking, bathing, and many other chores that require its use every day. In this article, we will discuss the parts of a cold water system, how to design and install it, how to maintain it, and what benefits it offers.
Components of a Cold Water System
A cold water system includes several vital parts:
- Source of Water Supply: A cold water system is based on either a city supply or a well from a private source. The source needs to comply with local regulations as regards water quality and safety.
- Pipes: Cold water pipes may be made of different materials, such as PVC, PEX, copper, and galvanized steel. Each type of material has its respective advantages and disadvantages regarding durability, cost, and installing the pipes.
- Valves: Gates and ball valves will aid in regulating the flow of water and will allow you to shut down parts of the system for maintenance or repairs.
- Faucets and Fixtures: The cold water supply connects you to fixtures such as sinks, showers, toilets, and many appliances including a dishwasher and a washing machine.
- Water Meter: City water systems have a water meter that measures the quantity of water that is utilized and billed. The pressure regulator will keep the water pressure safe and uniform throughout the system in an area with high water pressure.
Design Requirements
A good number of essential factors come into play when designing a cold water system.
- Water Demand: Determine how many people are going to make use of the water. This will enable you to find the size of piping and appropriate fixtures. Ensure that the design can hold the maximum usage during the peak times.
- Pipe Sizing: Proper sizing is required for pipes. This ensures proper flow of water, hence no loss of pressure. The required formulas and charts determine the diameter to be used in pipes, based on their length along with the number of related appliances that are to be joined with them.
- Layout: It should provide a proper layout so that the curvature does not result in too many bends and turns in the pipes that really delay the flow of water. Such a layout is also easy for installation and maintenance.
For example, if the pipes that house the cold water in cold regions are insulated, they can prevent further condensation causing the freezing to happen. This maintains the quality of water while preventing any form of damage to the plumbing system.
Installation Process
Setting up a cold water system is a multi-step process:
- Planning and Design: The planning and design process starts off with a comprehensive plan. This will include the pipe layout diagram; where the various fixtures should go and calculations for appropriate pipe sizes and flow rates.
- Excavation and Trenching: If a system connects to an underground water supply, then dig trenches to lay the pipes at the right depth.
- Pipe Installation: Lay the pipes just like in the installation plan. Ensure that you tie-in, connect, and support the pipe connections and supports so that they are not sagging or settling over time.
- Pressure Test: When you have completed installing the pipes, carry out a pressure test to check out for any leaks and ensure all the connections fit the fixture or appliances.
- Final Connections: When the testing is over, establish the last connections on the fixture and appliances to prepare the system to put it to use.
Maintenance of Cold Water Systems
Regular maintenance is very important to ensure a cold water system functions effectively and has a longer life. The following are some of the most important steps of the maintenance process:
- Regular Inspection: Leakages, rust and wears are checked periodically to prevent developing into more harmful problems later.
- Block Clearing: Sods may accumulate within the pipes and fully halt the water flow or slow them down. The system should be washed or cleaned periodically to avoid it happening.
- Inspect Valves and Fixtures: Valves and fixtures need to be checked to ensure that they function in the right way and can be used at a reasonable level of performance.
- Continuous Water Quality Monitoring: Carry out tests on the water quality at intervals to determine any contaminant and ensure that water has reached a quality suitable for human consumption.
Benefits of a Cold Water System
A good cold water system has the following benefits:
- Health and Hygiene: A sound cold water system gives you safe drinking water. Safe drinking water is necessary both for your health and hygiene.
- Comfort and Convenience: Cold water is critical for many daily uses such as cooking and bathing, making it an essential element in modern life.
- Energy Efficiency: The systems of cold water tend to require less energy than the hot water system and, consequently, could be saving you money on utilities.
There would thus be reduced water usage and conservation in cold water systems due to effective usage.
Pipe Sizing Formula for Cold Water Systems
Using the formula below based on flow rate and velocity in a cold water system:
Flow Rate (Q) in gallons per minute (GPM):
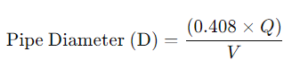
For residential systems, generally a minimum velocity of 5-7 feet per second (FPS) for water is recommended.
Formula:
Where:
- DDD = Diameter in inches
- QQQ = Flow rate in GPM
- VVV = Velocity in FPS
Sizing Chart for Cold Water Pipes
This is a General sizing chart for common pipe materials, based on a flow rate of 5-10 GPM and maintaining an average velocity of 5-7 FPS:
| Flow Rate (GPM) | Copper Pipe (Type L) | PVC Pipe | PEX Pipe |
| 1 | 1/2″ | 1/2″ | 1/2″ |
| 2 | 1/2″ | 1/2″ | 1/2″ |
| 3 | 1/2″ | 1/2″ | 1/2″ |
| 4 | 3/4″ | 3/4″ | 3/4″ |
| 5 | 3/4″ | 3/4″ | 3/4″ |
| 6 | 3/4″ | 3/4″ | 3/4″ |
| 8 | 1″ | 1″ | 1″ |
| 10 | 1″ | 1″ | 1″ |
| 15 | 1-1/4″ | 1-1/4″ | 1-1/4″ |
Conclusion
A plumbing system that provides safe, clean water access is considered essential for every household and commercial building. Knowing what its constituent parts are, how it should be designed, what the installation processes are, and what maintenance requirements exist, property owners will appreciate the importance of such a system. Providing proper planning and care, a cold water system can serve its purpose for many years, thus contributing to health, comfort, and convenience for its users.
FAQs
What is a cold water system?
A cold water system takes water directly from the mains, heats it, and sends it straight to where it’s needed. There’s no need for storage tanks. Since heating makes the water expand, an expansion vessel and a safety valve are used to control the temperature and pressure.
What is a cold water storage system?
This system is common in many commercial buildings. Water enters the building from a main supply and is stored in a tank. The water then flows by gravity from the tank to the areas where it’s needed, without any recirculation.
What is a cooling water system?
Cooling water systems in India usually have a storage tank, a pump, a pressure regulator, and a water treatment system. The storage tank holds the water, ensuring there’s a steady supply of cool water all day.
What is the principle of water cooling?
In a water cooling system, liquid (usually water) moves through pipes, absorbing heat from components and releasing it in a radiator. It works like a car’s engine cooling system, where coolant flows through the engine to the radiator.
Read More – Sanitary Drainage Systems Explained