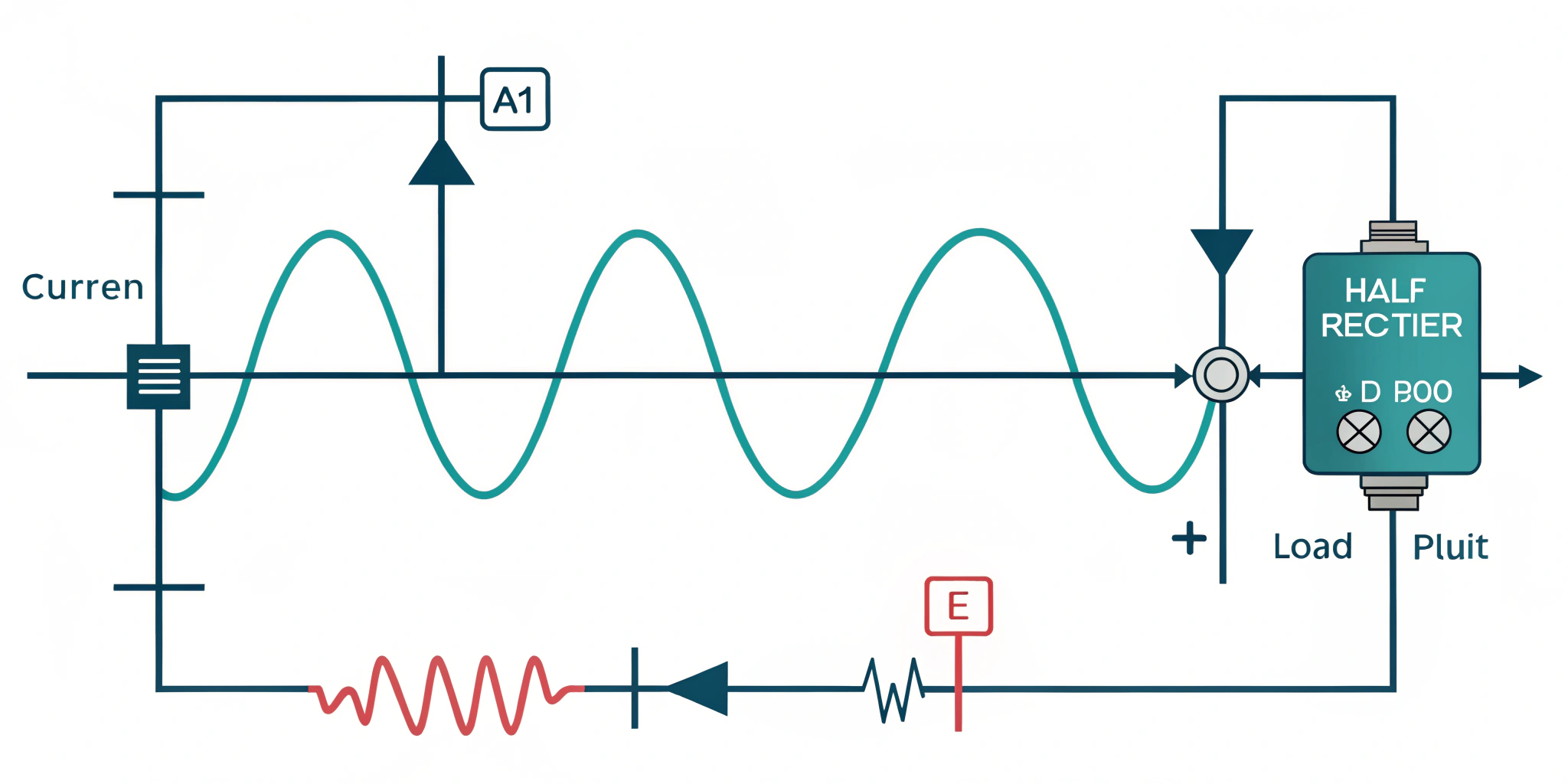
Half‑Wave Rectifier: A half‑wave rectifier converts AC into a pulsed DC output. It uses a single diode to pass one half of the input waveform. As a result, you get a series of positive (or negative) pulses instead of a smooth DC level. This simple circuit forms the basis of many power‑supply designs.
Circuit Diagram and Working
In a typical setup, you connect one diode in series with the AC source and the load resistor. During the positive half cycle, the diode conducts and allows current to flow through the resistor. Consequently, you see a voltage pulse across the load that matches the input peak minus the diode drop. During the negative half cycle, the diode blocks current. Therefore, the output stays at zero until the next positive cycle. By repeating this process, you obtain a pulsed DC signal that can feed simple electronics.
Half‑Wave Rectifier: Mathematical Analysis
You can predict the performance using a few key formulas. First, the average DC output voltage equals the input peak divided by π:
VDC = Vpeak / π
Next, the ripple factor measures how much AC variation remains:
ripple = √[(Irms² / Idc²) – 1]
Here, Irms and Idc are the RMS and average load currents. Finally, efficiency tells you how well the rectifier converts power:
η = (Pdc / Pac) × 100%
these simple equatians is helpful to select right components and predit the out put quality.
Key Formulas at a Glance
- VDC: Vpeak / π
- Ripple factor: √[(Irms² / Idc²) – 1]
- Efficiency: (Pdc / Pac) × 100%
Applications, Advantages & Limitations
Half‑wave rectifiers appear in low‑cost power supplies and peak detectors. They require only one diode and a minimal parts count. Moreover, they are easy to build and troubleshoot. However, their efficiency rarely exceeds 40 %, and they produce significant ripple. Therefore, you often add a filter capacitor to smooth the output. Even so, designers prefer full‑wave circuits for higher power and lower ripple applications.
By understanding these basic concepts, you can design or analyze simple DC supplies with confidence. Whether you test sensors or build battery chargers, the half‑wave rectifier remains a fundamental electronic building block.
READ ALSO ; SI System of Units – Comprehensive Guide