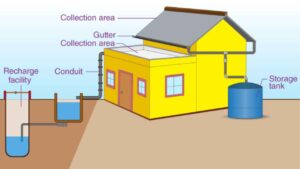
Rainwater harvesting is a straightforward method used to collect and store rainwater. It involves gathering rainwater from places like rooftops, parks, roads, and open areas, and then cleaning and storing it for later use. In this article, we will explore the different types of rainwater harvesting systems, their advantages, and some disadvantages, along with a diagram for better understanding.
Rainwater Harvesting Diagram
All living things, including plants, animals, and humans, need water to survive and perform various activities in their cells.
Imagine a world without water—it’s hard to picture, but we all use water daily for activities like cleaning, washing, bathing, cooking, drinking, and other home and industrial tasks.
Water is a precious, essential part of the ecosystem. Right now, we face a growing water shortage. This is mainly due to poor water conservation and pollution of water sources. Let’s stop wasting water and start saving it for future use.
Why is Rainwater Harvesting Important?
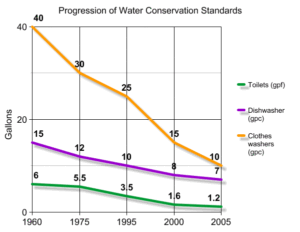
Rainwater harvesting is important for many reasons. One major reason is that we have already maximized water conservation inside our homes, so we need to explore outdoor options for more opportunities.
The graph below shows the water-saving progress made with indoor fixtures, thanks to government standards and innovations by fixture companies. As you can see, there isn’t much more we can do to increase efficiency with indoor fixtures.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting
Understanding the types of rainwater harvesting helps us choose the best system for our needs and learn the steps to implement it effectively.
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
This method collects rainwater directly from where it falls. The roof acts as the catchment area, and the water is collected from the roof of a house or building. The water can be stored in a tank or sent to an artificial recharge system. This method is cost-effective and, when done properly, helps increase the groundwater level in the area.
Surface Rainwater Harvesting
In urban areas, rainwater often flows away as surface runoff. This runoff can be captured and used to recharge aquifers with the right techniques.
How to Harvest Rainwater?
Rainwater harvesting systems include the following parts:
- Catchment: Collects and stores the rainwater.
- Conveyance system: Moves the collected water from the catchment to the recharge area.
- Flush: Removes the first rainwater, which may contain debris.
- Filter: Cleans the rainwater by removing pollutants.
- Tanks and recharge structures: Store the filtered water, making it ready for use.
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater using specially designed systems. These systems collect water from natural or man-made areas like rooftops, open spaces, rock surfaces, slopes, or treated land surfaces.
Several factors affect the amount of water you can harvest. Some important factors include:
- The amount of water that runs off
- The features of the catchment area
- Environmental impact
- Availability of technology
- Storage tank capacity
- The type, slope, and material of the roof
- The frequency, amount, and quality of rainfall
- The speed and ease of rainwater filtering into the ground to recharge groundwater.
Why Do We Harvest Rainwater?
Rainwater harvesting is a great way to help conserve water. Nowadays, the shortage of clean, good-quality water is a big concern. However, rainwater is pure and can be used for many purposes like irrigation, washing, cleaning, bathing, cooking, and even for the needs of animals.
Advantages of Rainwater Harvesting
Here are the benefits of the rainwater harvesting system:
- Low cost
- Reduces water bills
- Lowers water demand
- Decreases the need for imported water
- Helps conserve both water and energy
- Improves the quality and amount of groundwater
- Doesn’t need a filtration system for watering landscapes
- Simple to install and operate
- Reduces soil erosion, stormwater runoff, flooding, and water pollution from fertilizers, pesticides, metals, and other pollutants
- Provides a chemical-free, mineral-free water source for landscaping
Disadvantages of Rainwater Harvesting
Despite its advantages, rainwater harvesting has a few disadvantages, such as:
- Unpredictable rainfall
- Lack of proper storage systems
- Requires regular maintenance
- Needs some technical skills for installation
- No rain or limited rainfall can reduce the water supply
- Poor installation may lead to mosquito breeding and waterborne diseases
- Storage capacity can be a major limitation
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting represents a simple yet very effective method by which one can save water and reduce the reliance on traditional water sources. From this, money can be saved, ground levels improved, and the environment protected through this act of collecting and storing rainwater. However, this system has benefits as well as challenges such as unpredictability in the natural circumstance of rainfall and maintenance. However, if planned and installed properly, rainwater harvesting will become a very important tool for sustainable water management for us to ensure a cleaner, more reliable water supply for the future.
FAQs
What is the rainwater harvesting system?
Rainwater harvesting collects, stores, and purifies rainwater from rooftops, roads, and open spaces for future use.
What are the 7 types of rainwater harvesting?
The seven types are: Water Butt, Direct-Pumped, Indirect Pumped, Indirect Gravity, Gravity Only, Retention Ponds, and In-Ground Storage.
What are the benefits of the rainwater harvesting system?
Rainwater harvesting reduces erosion, controls stormwater runoff, and prevents scale and corrosion from hard water.
What are the methods of rainwater harvesting?
Rainwater is collected from the roof, filtered through pebbles and sand, and stored in a tank or sump.
Read More – Standpipe System Explained