Corrosion is when metals gradually separate in view of responses with air or water. This regular interaction makes things like extensions and lines more fragile after some time. Understanding erosion assists us with safeguarding these designs and guarding them for everybody.
Corrosion quietly destroys metal, causing harm that influences our regular routines — from debilitated extensions to broken pipelines. Understanding how corrosion functions assists us with caring more for structures, guaranteeing they stay solid and safe for everybody.
Remain with us to figure out what corrosion means for your general surroundings and why it makes a difference. By understanding this normal interaction, we can safeguard significant designs and settle on more brilliant decisions to keep our current circumstance protected and dependable.
The Basics of Corrosion

Corrosion is a characteristic cycle that slowly decays materials, especially metals, because of synthetic responses with their current circumstance. This cycle frequently results from the cooperation among metal and oxygen, framing oxides like rust on iron. Erosion is in excess of a straightforward response; it influences foundation, hardware, and any metal items presented to air or dampness.
Understanding its significant on the grounds that it influences businesses from development to transportation. The disintegration brought about by erosion can think twice about uprightness, prompting exorbitant fixes and potential security perils. Mindfulness and preventive measures are imperative to deal with this unavoidable issue.
Types of Corrosion

Corrosion comes in different structures, each with particular qualities:
- Uniform Corrosion: The most well-known type, where a metal surface breaks down equitably over the long run. It normally influences designs like pipelines and extensions.
- Pitting Corrosion: This type causes limited harm, prompting little openings or pits. It is especially perilous on the grounds that it is more diligent to distinguish and can prompt unexpected disappointments.
Galvanic corrosion happens when two disparate metals come into contact in a conductive climate. This type speeds up the debasement of one metal while safeguarding the other. Fissure erosion frequently influences regions where dampness is caught, like joints and darted segments, while intergranular corrosion focuses on the limits inside a metal’s construction, normally seen in inappropriately treated tempered steel.
Causes of Corrosion
It is essentially determined by synthetic and electrochemical cycles. The presence of dampness and oxygen is the most widely recognized cause, however different factors likewise contribute:
- Ecological Circumstances: High moistness, salt in the air, and contaminations can speed up the corrosion cycle.
- Material Organization: Metals that are less impervious to corrosion, similar to press, are more defenseless contrasted with erosion safe composites like treated steel.
Electrolytes, like those tracked down in seawater, work with electron stream, accelerating the response. The underlying model, including hard-to-arrive at regions, can advance limited erosion, particularly when dampness collects.
The Electrochemical Nature of Corrosion
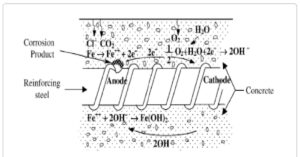
Erosion is on a very basic level an electrochemical interaction including the exchange of electrons. For instance, during the rusting of iron, the metal goes about as the anode, losing electrons, while oxygen in water fills in as the cathode. This outcomes in the arrangement of iron oxide, which is permeable and debilitates the fundamental metal.
The oxidation-decrease cycle supports this interaction, with oxidation including electron misfortune and decrease including electron gain by another substance, ordinarily oxygen. This cycle go on as long as the circumstances stay positive for electron move, propagating the harm.
Economic and Safety Impacts of Corrosion
The monetary ramifications of corrosion are significant, with worldwide expenses adding up to trillions of dollars every year. Ventures dependent on metal framework, including oil, gas, and transportation, apportion huge assets to counter erosion. Support, fix, and preventive techniques are progressing costs that safeguard these speculations.
The security outcomes are similarly disturbing. Consumed scaffolds, structures, and pipelines present extreme dangers, as disappointments can happen abruptly. Such episodes imperil lives and upset monetary exercises, underlining the requirement for vigorous enemy of erosion measures and systems.
Protective Methods Against Corrosion
Forestalling corrosion requires a diverse methodology, focusing on either the climate or the metal surface itself:
- Defensive Coatings: Applying paints, stains, or concentrated coatings frames a boundary to impede dampness and air from arriving at the metal.
- Cathodic Security: This technique interfaces the vulnerable metal to a more responsive “conciliatory” metal. The conciliatory metal consumes all things considered, safeguarding the principal structure.
The utilization of corrosion safe materials like treated steel, which contains chromium, offers innate security because of the development of a meager oxide layer. Plan enhancements that advance seepage and cutoff dampness collection can likewise assume a key part in decreasing erosion gambles.
Technological Advancements in Corrosion Control
Arising innovations have acquainted new ways with battle erosion. Brilliant coatings, implanted with sensors and corrosion inhibitors, are acquiring ubiquity. These coatings can distinguish early indications of erosion and deliver defensive synthetics to slow the interaction.
Nanotechnology has additionally tracked down its direction into erosion counteraction. By adding nanoparticles to defensive coatings, the obstruction properties are upgraded, making them more impervious to harm. These headways demonstrate a shift toward proactive, keen arrangements in the battle against corrosion.
Monitoring and Early Detection
Checking erosion should be considered ordinary since it is the major check of keeping up with the framework. Safety checks and non-destructive tests including ultrasound help in the definition of weak parts before catastrophic failure. Various electrical opposition tests and other sensors can also detect that which shows the beginning phase corrosion.
A good upkeep procedure includes both routine cleansing and redeposition of protectant coatings. It helps prevent erosion and reduce the likelihood of untimely disappointments on the way forward. Such endeavors can help extend the lifespan of resources and ensure that they are both safe and affordable for the organizations in question.
How Do We See Corrosion in the Real World?
It affects all articles that are taken as normal and basic structures. For instance, Span looks at the Silver Extension breakdown in 1967, which illustrates how erosion can be destructive. This occurrence caused by pressure corrosion breaking did make this point that ordinary examination and maintenance play an important role in preventing such disasters.
Pipeline corrosion remains a significant hurdle to endeavors such as oil & gas. These enterprises ensue proactively in enemy corrosion processes such as coatings, cathodic protection and regular checks in a bid to reduce risks and compliance with safety measures.
Challenges to the management of corrosion
However, managing the pace also does not come without its challenges – oversight of deterioration includes. Cruel conditions, for instance those in seaside areas, makes it hard to prevent erosion from taking its full course. Further, the implementation cost of an optimal range of defense measures against erosion could be hefty, cost-prohibitive for many small companies or certain public projects.
Corrosion the board additionally expects talent experts to plan, implement and maintain reliable prevention equipment physically as well. Confidence in emerging and getting ready guarantees that fresher, more draw-in strategies proceed to turn up and interdisciplinary work addresses these difficulties.
Conclusion
Careful analysis of the underlying science in corrosion is critical in containing challenges associated with corrosion in various industries. It also surfaces enormous financial burdens in costing the lifetime of designs as well as of apparatuses not forgetting the impacts it has on the environment. By focusing on some of the factors that are not easily seen, including the electrochemical responses, and perceiving the factors that contribute to it, such as, the natural conditions arrangements can be made in order to reduce its effects.
Invigorating examination into The Science Behind Erosion incites architects, makers, and researchers to drive creative safeguard courses of action, from erosion secure materials to advanced coatings, and observing frameworks. Through this kind of information, ventures can ensure that there is improved maintenance, enhanced health and safety and more importantly efficient operations. With the proper balance between avoidance and innovation performance, what’s in store ensures more effective dealing with the ever-recurring challenge of protection of assets while enhancing sustainability.
FAQs
What is the science behind corrosion?
Corrosion happens when metals break down due to chemical reactions with air or water. This process involves metal losing electrons and forming compounds like rust, which weakens the metal.
What is the scientific explanation of corrosion?
Corrosion is an electrochemical reaction where metals react with oxygen and moisture, causing oxidation. This leads to the formation of oxides, like rust, which damages the metal over time.
What are the general science principles behind corrosion?
The main principle of erosion is oxidation, where metals lose electrons when exposed to air or water. This creates a chemical reaction that forms oxides and weakens the metal.
What is the theory behind corrosion?
Erosion theory explains that metal atoms lose electrons and form oxides through electrochemical reactions. This process happens when metals react with oxygen, water, or other chemicals.
What is the principle of corrosion?
This principle is based on the metal losing electrons in a reaction with oxygen and moisture, creating oxides that weaken the structure and cause damage over time.
READ MORE: Understanding Refrigerant Container Colors





















