ELECTRICAL
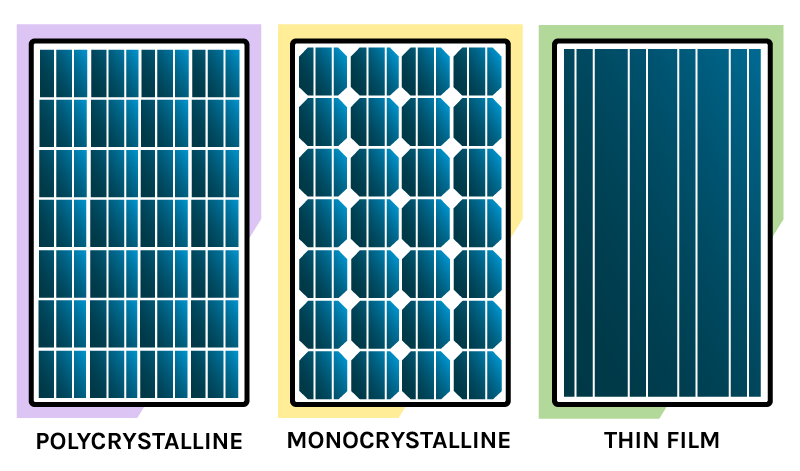
Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline & Thin-Film Solar Panels
Introduction: The selection of proper solar panel stands as the key decision for solar energy adopters. The following piece examines monocrystalline and polycrystalline along ...
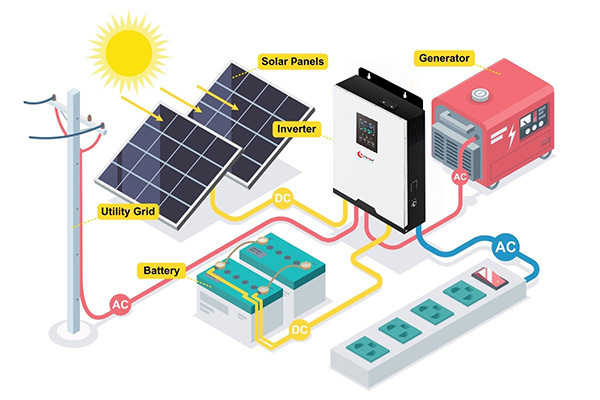
Can You Combine AC and DC Ground in a Solar Installation?
Introduction Can you combine AC and DC ground in a solar installation? Safety and system efficiency remain the primary issues during the establishment of ...
What is Volt (V)?
The fundamental role that electricity plays in everyday life depends heavily on the important concept known as Volt (V). But what is Volt (V)? ...
Casing Capping Wiring Guide
Introduction The traditional electrical wiring approach named Casing-capping wiring provides a safe foundation while showing an aesthetic appearance through its protective design. The wiring ...
How Electricity Works
Introduction Electricity stands as the most significant discovery in history. The worldwide distribution of electrical power enables our residential buildings, industrial facilities, and technological ...
Auto Reclosing Scheme of Transmission System: Working, Types, and Benefits
Introduction Reliability and continuity of services are essential in modern power transmission networks. The Auto Reclosing Scheme is one of the best techniques for ...
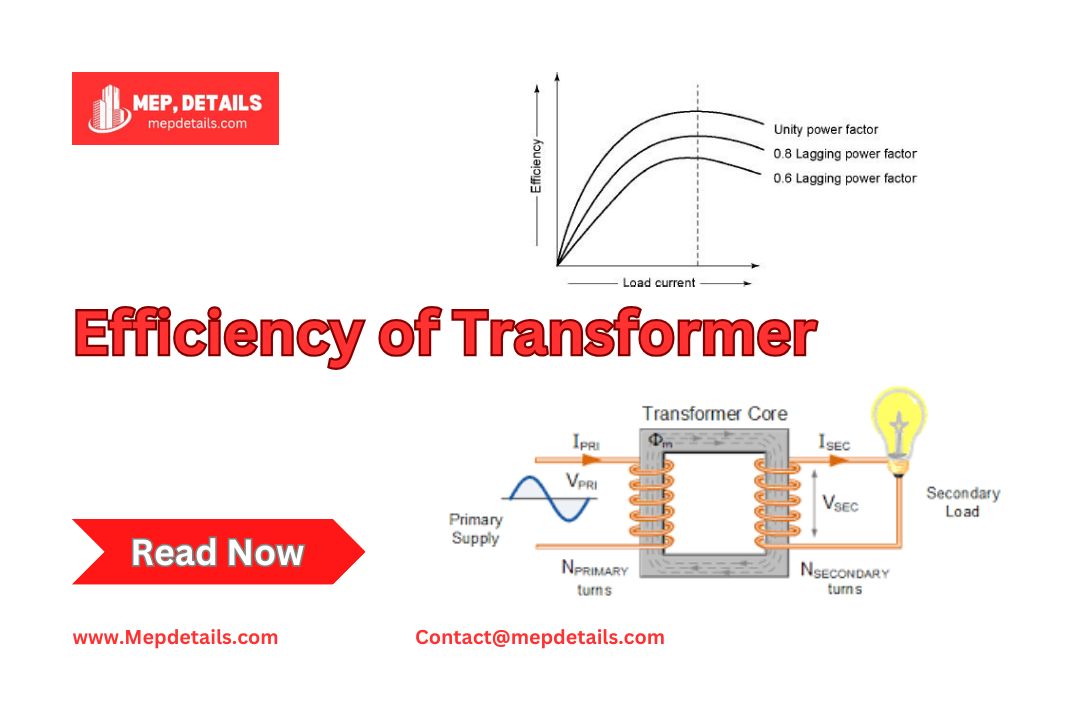
Efficiency of Transformer
Transformer efficiency is a key factor to consider when choosing a transformer. It shows how well a transformer converts electrical energy with minimal losses. ...
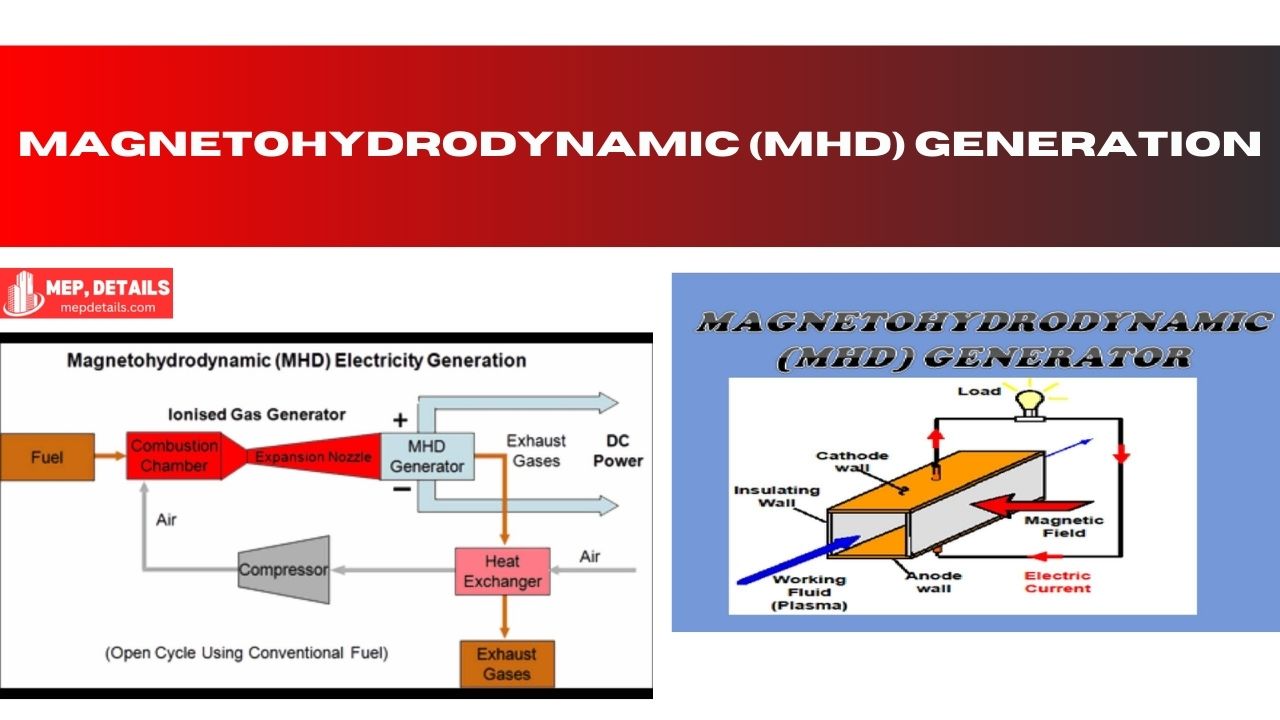
MHD Generation: Revolutionizing Energy Production
MHD generation converts hot and moving gaseous or liquid substances in a magnetic field into electricity. This application is considered revolutionary since it delivers ...
Static Kramer Drive: Working, Construction, and Characteristics
The Static Kramer Drive controls the speed of an induction motor by injecting opposite-phase voltage into the rotor circuit. This injected voltage increases the ...
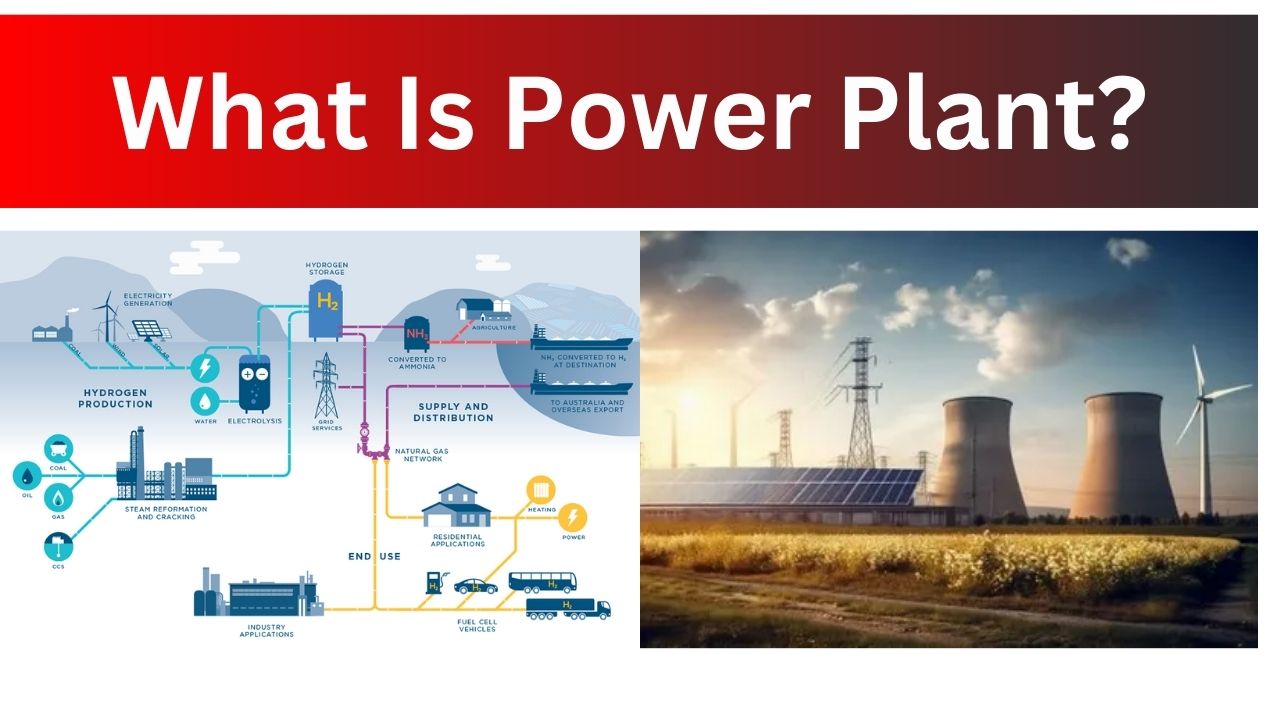
Power Plant: Types, and Their Role in Modern Energy Production
A power plant is an office that makes power to control homes and organizations. It turns energy sources like coal, water, or daylight into ...