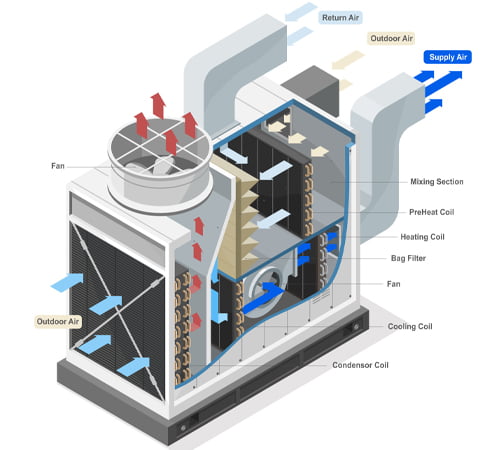
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems: A Comprehensive Overview
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are a vital component of building infrastructure, providing thermal comfort and indoor air quality to occupants. These systems regulate temperature, humidity, and airflow to create a comfortable environment, regardless of external conditions. Let’s explore the key details of HVAC systems in-depth:
Heating:
Heating is a fundamental aspect of HVAC systems, especially in colder climates. HVAC systems employ various heating methods:
- Furnaces: Furnaces are common heating systems that use natural gas, oil, electricity, or other fuels to generate heat. The heat is then distributed through ductwork and vents.
- Boilers: Boilers heat water to produce steam or hot water, which is then circulated through radiators, baseboards, or radiant floor systems to warm spaces.
- Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are versatile systems that can provide both heating and cooling by transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. They are especially efficient in moderate climates.
Ventilation:
Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining indoor air quality and reducing the concentration of pollutants. Ventilation systems ensure a continuous supply of fresh air while removing stale air. There are different ventilation strategies:
- Natural Ventilation: Relies on natural airflow through windows, doors, and vents to exchange indoor and outdoor air. This method is energy-efficient but less controllable.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Utilizes fans and ductwork to mechanically introduce fresh air and exhaust stale air. This method allows for better control and filtration of indoor air.
Air Conditioning:
Air conditioning is essential for cooling indoor spaces, especially in warmer climates. Cooling methods include:
- Central Air Conditioning: Central AC systems cool air through a refrigeration cycle, distributing the cooled air through ducts and vents.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: These systems consist of an outdoor unit connected to indoor air-handling units. They provide individualized cooling to specific zones.
- Evaporative Coolers: Common in dry climates, evaporative coolers use water evaporation to cool and humidify the air. They are energy-efficient but less effective in humid conditions.
HVAC Controls:
Sophisticated controls are essential for optimizing HVAC system performance and energy efficiency:
- Thermostats: Thermostats regulate indoor temperature by sensing ambient conditions and adjusting heating or cooling systems accordingly.
- Programmable Thermostats: These allow occupants to preset temperature settings based on time, optimizing energy use when spaces are unoccupied.
- Smart Thermostats: Internet-connected smart thermostats offer remote control and learning capabilities, adapting to occupants’ preferences and adjusting settings for energy savings.
Energy Efficiency:
Energy efficiency is a significant focus in modern HVAC system design:
- Variable Speed Motors: These motors adjust fan and compressor speeds based on demand, reducing energy consumption.
- Zoning: Zoning divides a building into different areas with independent temperature control, optimizing comfort and energy use.
- Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) and Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV): These systems recover heat from exhaust air to preheat incoming fresh air, minimizing energy loss.
Sustainability and Innovations:
HVAC systems are evolving to align with sustainability goals:
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: These systems use the stable temperature of the ground as a heat source in winter and a heat sink in summer, increasing efficiency.
- Solar-Powered HVAC: Solar panels can power HVAC systems, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources.
- Demand-Controlled Ventilation: Systems sense occupancy levels and adjust ventilation rates accordingly, optimizing energy use while maintaining indoor air quality.
Conclusion:
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are integral to modern buildings, providing comfort and indoor air quality. Advances in technology, coupled with an increased emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, are driving innovation in HVAC system design and operation. A well-designed HVAC system ensures occupants’ comfort, contributes to energy savings, and aligns with broader environmental goals.