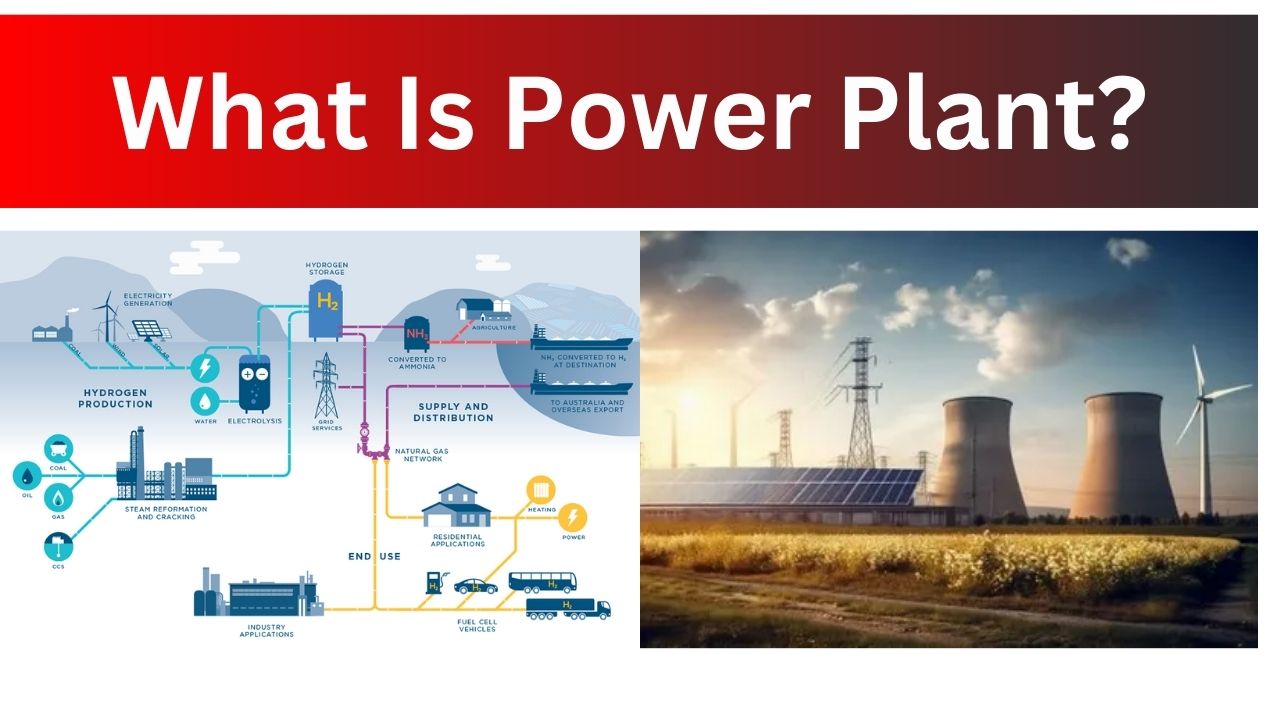
A power plant is an office that makes power to control homes and organizations. It turns energy sources like coal, water, or daylight into power. Power plants are significant for day to day existence, assisting us with remaining associated and useful.
Envision existence without lights, telephones, or PCs — difficult to picture, correct? Power plants make this multitude conceivable by transforming fuel or regular assets into power. They keep our reality moving, controlling all that we depend on each day.
Remain with us as we investigate how power plants work, the sorts they come in, and their part in our lives. You’ll comprehend the reason why these energy monsters are so significant and how they keep our reality chugging along as expected.
Power Plant Types and Their Distinct Roles
Force age relies upon a grouping of power plants, each using different methodologies to convey power. The most broadly perceived types integrate thermal power plants, hydroelectric power stations, nuclear power plants, and harmless to the ecosystem power workplaces like breeze and sun arranged farms. Thermal power plants make energy by consuming oil based goods like coal, oil, or combustible gas to convey steam, which drives turbines related to generators. These plants expect an immense part in the overall energy mix due to their high energy yield and spread out system, regardless of the way that they add to ozone exhausting substance releases.
Hydroelectric power plants tackle the dynamic energy of streaming water to make power. These workplaces are worked near water sources like streams and dams and rely upon the improvement of water to turn turbines. Hydropower is seen as one of the most useful manageable power sources, offering a sensible choice as opposed to oil subsidiary based power age. Regardless, regular concerns associated with organic framework interferences and water use ought to be thought of
Functions of Power Plants in Energy Production
A power plant can be defined as an establishment that has the primary function of transforming distinct sources of energy into usable electrical energy in order to be distributed using electrical grids. Turbines in thermal power plants are driven by steam created through heat energy. This change process involves a few stages such as fuel ignition, heat transfer, and mechanical energy conversion. This process guarantees an uninterrupted supply of power, which meets a significant demand for industrial and domestic consumption.
Nuclear power generation plants work by utilizing energy released during atomic fission. When atoms of either uranium or plutonium are split, an enormous amount of energy is released, which is generated to produce steam to drive turbos. Nuclear energy is very effective and produces greenhouse gasses in negligible quantities, there are issues with regards to management of radioactive wastes and hazards so far potential security threats have to take advanced safety measures. However, Nuclear power is essential and adds up to the energy grid due to production reliability and consistency.
Renewable Energy Power Plants: A Growing Segment

Environmentally friendly power plants, including wind, sun oriented, and geothermal offices, assume an undeniably significant part in supportable energy creation. Wind power plants convert active energy from wind into mechanical power utilizing enormous turbines. These turbines pivot and produce power with next to no immediate emanations. The adaptability of wind ranches, from little neighborhood arrangements to enormous seaward establishments, broadens the energy portfolio and diminishes dependence on petroleum products.
Sun based power plants catch daylight through photovoltaic cells or sunlight based warm frameworks. Photovoltaic (PV) cells straightforwardly convert daylight into power, while sun based warm frameworks use daylight to warm a liquid that produces steam for turbine activity. Sunlight based energy is bountiful and inexhaustible, yet its viability can be restricted by weather patterns and sunshine accessibility. In spite of this, progressions in energy capacity innovation are making sunlight based power more dependable and generally embraced in current matrices.
Key Advantages and Challenges of Different Power Plants
- Thermal Power Plants:
- High energy output and reliability.
- Dependence on finite fossil fuels leading to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nuclear Power Plants:
- Low greenhouse gas emissions and significant energy output.
- Risks related to radioactive waste and nuclear accidents.
- Hydroelectric Power Plants:
- Renewable and efficient energy source.
- Potential environmental impacts on aquatic ecosystems and water management.
- Renewable Energy Power Plants (Wind & Solar):
- Environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Variability in energy production due to weather conditions.
Hydroelectric and renewable energy power plants often face challenges in terms of initial setup costs and location constraints. Building a dam or a wind farm requires extensive planning, environmental assessments, and investment. However, these facilities offer long-term benefits such as lower operational costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
The Job of Force Plants in Present day Energy Lattices
Power plants are the groundwork of current energy organizations, ensuring the trustworthiness and relentless nature of force supply. They fill in as fundamental power sources, giving constant energy to fulfill benchmark need, known as “baseload power.” Warm and nuclear power plants are consistently used for baseload due to their ability to deliver colossal measures of energy dependably. This ensures that metropolitan districts, undertakings, and principal organizations get ceaseless power.
Peaking power plants, as vaporous petroleum turbines, are expected to supply additional power during seasons of allure, known as “top weight.” These plants can quickly start and stop exercises, making them ideal for dealing with unforeseen floods in energy use. Harmless to the ecosystem power sources, while critical, every now and again supplement the network instead of going probably as fundamental power providers in light of their variable nature. Notwithstanding, as energy amassing advancement drives, maintainable plants are dynamically adding to both base and apex loads.
Integration of Power Plants with Emerging Technologies
Present day power plants are coordinating state of the art advancements to further develop productivity and lessen ecological effects. High level control frameworks, information examination, and computer based intelligence fueled checking permit administrators to advance power creation and anticipate gear disappointments before they happen. These advancements upgrade plant execution, decrease free time, and increment the general proficiency of energy change.
Carbon catch and capacity (CCS) frameworks are being integrated into nuclear energy stations to relieve ozone harming substance outflows. CCS innovation catches carbon dioxide created during ignition and stores it underground, keeping it from entering the air. Likewise, half and half power plants, which consolidate conventional and sustainable power sources, are building up some momentum. For example, a gas-terminated power plant can be enhanced with sunlight based chargers, making a more adaptable and maintainable energy creation framework.
Environmental and Economic Impacts of Power Plants

Power plants have huge natural and monetary ramifications. Petroleum derivative based power plants add to air contamination and ozone harming substance outflows, which are connected to environmental change and wellbeing concerns. Progressing to cleaner energy sources diminishes these effects and line up with worldwide environment objectives. The monetary effect of force plants reaches out to work creation, framework advancement, and energy evaluating. Huge scope power plants require gifted specialists, adding to work open doors in areas with energy creation offices.
On the financial front, sustainable power plants have shown to be cost-serious over the long run. The declining cost of wind turbines and sunlight based chargers has made sustainable power more reasonable, boosting state run administrations and confidential areas to put resources into green advancements. This shift upholds energy enhancement as well as helps in accomplishing reasonable monetary development.
Future Prospects and Sustainability Goals
The fate of force plants lies in adjusting proficiency, maintainability, and mechanical advancement. With expanding consciousness of ecological worries, there is areas of strength for a toward environmentally friendly power reception. State run administrations all over the planet are setting aggressive focuses to transition away from coal and other dirtying energy sources, zeroing in rather on cleaner options like breeze, sunlight based, and hydrogen power devices. Energy capacity arrangements, for example, enormous scope battery establishments, assume a significant part in supporting these drives by putting away excess energy for use during low creation periods.
The idea of microgrids, limited scope energy networks that work freely or close by the fundamental power matrix, is building up forward movement. Microgrids frequently consolidate environmentally friendly power sources and can improve the strength of neighborhood energy supply during blackouts or cataclysmic events. This approach upholds the decentralization of energy creation, advancing energy freedom and maintainability at the local area level.
Conclusion
Power Plant: Types, Capabilities, and Their Job in Present day Energy Creation show how fundamental these offices are for dependable energy supply. From warm and atomic plants to sustainable sources like breeze and sun oriented. In each type contributes interestingly to the energy framework, guaranteeing power arrives at homes and businesses. These power plants support day to day existence, modern development, and mechanical headway.
Looking forward, Power Plant: Types, Capabilities, and Their Job in Present day Energy Creation will keep developing as we move towards cleaner and more manageable energy arrangements. Coordination of environmentally friendly power, energy capacity frameworks, and shrewd innovation will shape the fate of force age. With advancement and ecological concentration, power plants will assume a significantly larger part in gathering worldwide energy needs. While safeguarding the planet for people in the future.
FAQs
What are the types of power plants?
Thermal, nuclear, hydroelectric, solar, wind, and geothermal power plants.
What are the functions of a power plant?
Convert energy from fuel sources into electrical energy for distribution and use.
What are the 3 main sources of energy for different types of electric power plants?
Fossil fuels (coal, natural gas), nuclear energy, and renewable sources (solar, wind).
What type of power plant uses?
Depends on location and energy needs; can include fossil-fuel plants, nuclear reactors, or renewable energy facilities.
What is the most common type of power plant?
Thermal power plants, primarily using coal or natural gas.
ALSO READ IT: Cogeneration: How It Works and Its Key Benefits