The size of your home informs the size of your heating and cooling units—but it will also determine how large your duct sizes need to be. To accurately gauge the size of your ductwork, you will need to precisely measure the square footage of not just your house as a whole, but the size of each room, as well.
Since the size of your ductwork can increase or lower this measurement, you’ll have to find the necessary CFM for each room before you can get the right duct size for each space.
- Cubic Feet Per Minute = (HVAC Unit Tons x 400) / total square footage of home.
- Calculate for each individual room.
RECTANGULAR DUCT FORMULA
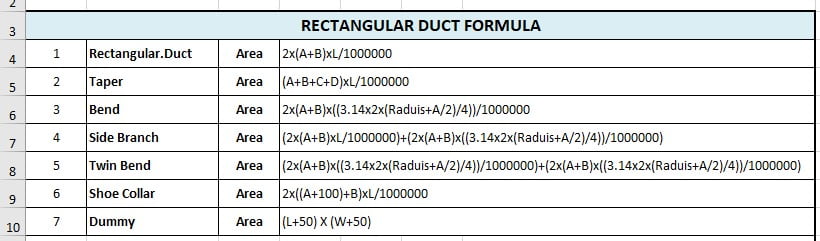
1 Rectangular.Duct Area 2x(A+B)xL/1000000
2 Taper Area (A+B+C+D)xL/1000000
3 Bend Area 2x(A+B)x((3.14x2x(Raduis+A/2)/4))/1000000
4 Side Branch Area (2x(A+B)xL/1000000)+(2x(A+B)x((3.14x2x(Raduis+A/2)/4))/1000000)
5 Twin Bend Area (2x(A+B)x((3.14x2x(Raduis+A/2)/4))/1000000)+(2x(A+B)x((3.14x2x(Raduis+A/2)/4))/1000000)
6 Shoe Collar Area 2x((A+100)+B)xL/1000000 7 Dummy Area (L+50) X (W+50)
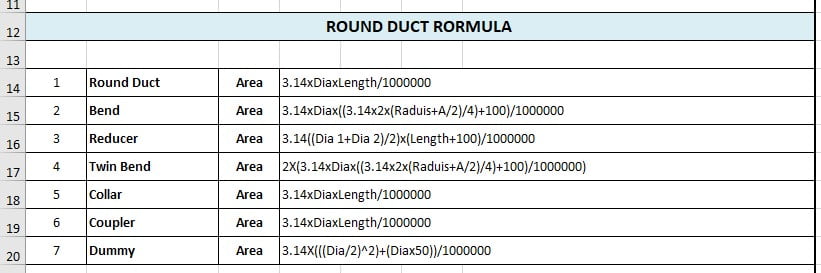
ROUND DUCT RORMULA
OVEL DUCT FORMULA
| 1 | Oval Duct | Area | 2x(A-B)+(3.14xB)xLength/1000000 | |||
| 2 | Oval Reducer | Area | (A-B)+(C-D)+(3.14XB/2)+(3.14XD/2)X(length+100)/1000000 | |||
| 3 | Oval Bend | Area | 2x(A-B)+(3.14xB)x(3.14x2x((150+A/2)/4)+100)/1000000 | |||
| 4 | Oval Coupler | Area | 2x(A-B)+(3.14xB)xLength/1000000 | |||
| 5 | Oval Dummy | Area | ((((A-B)XB)+(3.14X(B/2)^2))+((2X(A-B)+(3.14XB))X50))/1000000) | |||











Clear, concise, and very informative — great job!
Thanks for sharing! I found this article really helpful.
Great post! I really enjoyed reading this article.
I have been checking out a few of your articles and it’s pretty nice stuff. I will definitely bookmark your website.
Your content always feels like conversation with trusted friend. This post made me pause